Hot tag
Popular search
Complete Radio Station Equipment Package You Should Have for FM Broadcasting
Radio station equipment is essential for delivering high-quality audio content to listeners. It consists of studio and broadcasting components that work together to ensure captivating programming.

From audio mixers to FM transmitters and antennas, these advancements in technology have enabled more sophisticated and efficient broadcasting capabilities. Explore this article to discover the main types of radio station equipment and where to find the best options for your station's needs. Let's dive in!
Sharing is Caring!
I. How Does an FM Radio Station Work?
An FM radio station operates through a series of steps that involve recording sounds, adjusting audio quality, transmitting audio signals, processing the signals, and finally broadcasting the FM signals. Here's a detailed explanation:
Step 1: Recording the Sounds
At an FM radio station, DJs, workers, or singers record their voices, music, or other audio content using microphones and software installed on computers. This allows them to capture the desired sounds and create digital audio files.
Step 2: Adjusting the Sounds
Audio tuners work on the recorded audio files using audio devices such as audio mixers. They adjust various aspects like volume levels, equalization, and other audio enhancement techniques to improve the overall sound quality and ensure a pleasant listening experience.
Step 3: Transmitting Audio Signals
Once the recording and adjustment processes are complete, the audio signals are transmitted to the FM broadcast transmitter. This transmission can occur through RF cables or a studio transmitter link, depending on the physical location of the studio station and the FM radio station.
Step 4: Processing the Audio Signals
As the audio signals pass through the FM broadcast transmitter, they undergo several processing steps. These include reducing noise in the audio signals, amplifying the power of the signals, converting them into analog signals, and then modulating them into FM signals. The transmitter prepares the audio content for broadcast over the FM frequency.
Step 5: Broadcasting the FM Signals
The processed FM signals are then sent to FM antennas. These antennas convert the electrical current representing the FM signals into radio waves. The FM transmitting antennas broadcast these radio waves outward in a specific direction, allowing the FM signals to propagate through the atmosphere.
Listeners within the coverage area of the FM radio station can then tune their FM receivers to the correct frequency and receive the transmitted signals through their radios, enabling them to enjoy the audio content being broadcast by the FM station.
This is a basic overview of how an FM radio station operates. It involves capturing and adjusting sounds, transmitting and processing audio signals, and finally broadcasting the FM signals through antennas to allow listeners to tune in and enjoy the content.
II. Complete FM broadcasting station equipment list
When setting up an FM broadcasting station, it is essential to have the right equipment to ensure smooth transmission of radio signals, including the choice of FM transmitter power level. Some broadcasters may opt for a lower power FM transmitter to cater to a localized area, while others may choose a medium or high power FM transmitter for broader coverage. These variations in equipment reflect the differing coverage needs of FM radio stations, ensuring they have the appropriate equipment to reach their target audience effectively.
1. FM Transmitter
An FM transmitter is the core component that generates and amplifies the FM signal before transmitting it to the antenna. FM transmitters come in various power levels, including low power (typically up to a few hundred watts), medium power (ranging from a few hundred watts to a few kilowatts), and high power (several kilowatts to megawatts):
- Low Power FM Transmitter: Low power FM transmitters are designed for shorter range transmissions. They typically have a transmission power ranging from a few watts to tens of watts. Low power FM transmitters are commonly available in both rack-type and compact-type designs. They are suitable for applications where the coverage area is relatively small, such as drive-in church broadcasting, drive-in parking lots, neighborhood radio stations, or campus radio stations. The coverage range of a low power FM transmitter can vary depending on factors such as antenna height, terrain, and surrounding obstructions, but it generally ranges from a few hundred meters to a few kilometers.
- Medium Power FM Transmitter: Medium power FM transmitters are intended for broader coverage areas compared to low power transmitters. They typically have a transmission power ranging from several tens to hundreds of watts. Medium power FM transmitters are available in both rack-type and compact-type designs. They find applications in community radio stations, small regional broadcasters, local commercial stations, and event broadcasting. The coverage range of a medium power FM transmitter can span several kilometers to tens of kilometers, depending on factors such as antenna height, transmission power, terrain, and surrounding interference sources.
- High Power FM Transmitter: High power FM transmitters are designed for extensive coverage areas. They have a transmission power ranging from several hundred watts to several kilowatts or even megawatts. High power FM transmitters are typically rack-type systems due to their higher power requirements and complexity. They are used by large commercial FM radio stations, national broadcasters, and metropolitan radio stations. The coverage range of a high power FM transmitter can extend over a large geographic area, spanning tens to hundreds of kilometers, depending on factors such as transmission power, antenna height, terrain, and surrounding interference sources.
2. FM Antenna System
- FM Antenna: This is the component that radiates the FM signal into the surrounding area. FM antennas can come in different types, such as dipole, circularly polarized, panel, or Yagi antennas. The choice of antenna type depends on factors such as coverage requirements, signal propagation characteristics, and desired directionality. FM antennas have specifications related to frequency range, gain, impedance, and bandwidth, which can vary based on the desired coverage area and antenna type. The power handling capability of the antenna depends on its construction and materials used. Antennas can be either directional (providing focused coverage in a specific direction) or omnidirectional (radiating the signal equally in all directions).
- Coaxial Cable: Coaxial cables are used to connect the FM transmitter to the antenna. These cables have specifications such as impedance (typically 50 or 75 ohms), shielding effectiveness, and frequency range. The cable specifications should match the FM broadcasting requirements and the overall system impedance.
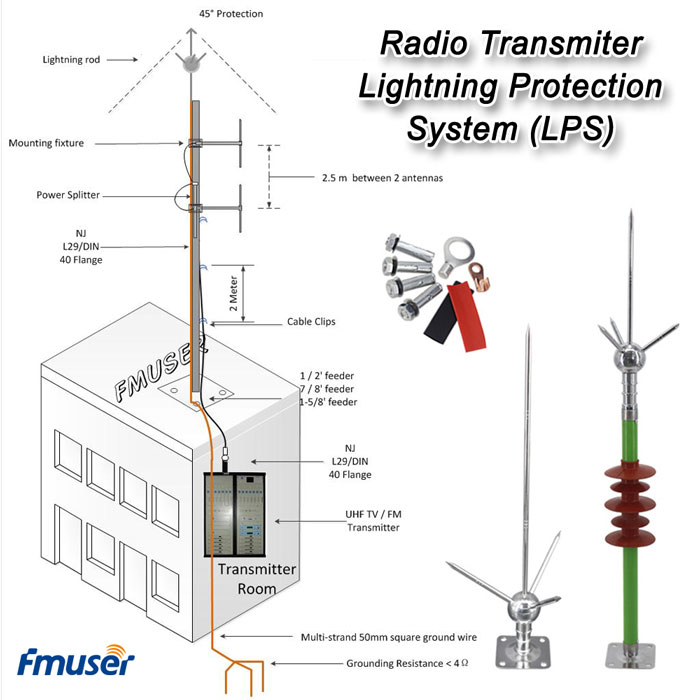
- Lightning Arrestor: Lightning arrestors are devices used to protect the FM antenna and associated equipment from damage caused by lightning strikes. They typically have specific voltage ratings and surge handling capabilities to dissipate and divert lightning-induced currents safely.
- Grounding Kit: Grounding kits include necessary components to establish a proper electrical grounding system for the FM antenna and equipment. These kits ensure proper grounding and bonding to protect against electrical faults and lightning strikes. The specifications may include the type of grounding conductor, connectors, and grounding impedance requirements.
- Broadcast Tower: Broadcast towers are structures that support the FM antenna at an elevated height. These towers have specifications related to height, load-bearing capacity, wind load resistance, and construction materials. The tower specifications should comply with local regulations and support the specific antenna and associated equipment.
- Antenna Mounting Hardware: Antenna mounting hardware consists of brackets, clamps, and other components used to securely mount the FM antenna. The specifications may vary depending on the antenna type, tower structure, and environmental conditions. They ensure proper and stable installation of the antenna.
- Dummy Load (for testing purposes): RF Dummy loads are used for testing and calibrating the FM transmitter without radiating the signal. They are typically designed to match the transmitter's impedance and power requirements. Dummy loads allow for accurate testing and measurement without broadcasting the signal.
- Rigid Coaxial Transmission Line and Parts: Rigid coaxial transmission lines consist of various components that work together to efficiently transmit the FM signal from the transmitter to the antenna. These components include the inner support, which provides mechanical stability and alignment for the inner and outer conductors. The flange adapter connects the line to other equipment securely. The outer sleeve acts as a protective layer for the transmission line, ensuring durability. Elbows enable directional changes, allowing the line to navigate obstacles or tight spaces. Couplers join separate sections of the transmission line, maintaining signal continuity. Together, these components ensure low loss and efficient signal transmission throughout the rigid coaxial transmission line.
3. Safety Protection System
- Lightning Protection System: A lightning protection system is designed to safeguard the FM radio station and its equipment from damage caused by lightning strikes. It typically includes lightning rods, grounding systems, and surge protection devices. While lightning protection is important for all FM radio stations, the specific requirements may vary based on location, weather conditions, and the susceptibility of the equipment to lightning-induced damage.
- Grounding System: A grounding system ensures that all electrical equipment and structures at the FM radio station are properly grounded. It helps to divert electrical faults and surges to the ground, preventing damage to the equipment and ensuring the safety of personnel. The grounding system should comply with electrical codes and regulations to provide effective protection.
- Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS): A UPS provides backup power during electrical outages or disruptions. It ensures that critical equipment, such as transmitters or automation systems, remains operational until the primary power source is restored or switched to a backup generator. The need for a UPS can vary based on the importance of continuous operation and the availability of backup power sources in the specific FM radio station.
- Surge Protector: Surge protectors are devices designed to absorb and divert excessive voltage spikes or surges. They protect sensitive equipment from damage caused by power surges or transient voltage events. The requirement for surge protectors may depend on factors such as the susceptibility of the equipment to voltage fluctuations, the power quality in the area, and the level of protection desired.
- Fire Suppression System: A fire suppression system is used to detect and suppress fires in the FM radio station. It includes fire detectors, alarms, and suppression agents like sprinklers or gas-based systems. The need for a fire suppression system depends on factors such as the size of the facility, regulatory requirements, and the presence of valuable equipment or archives.
- Alarm System: An alarm system consists of sensors, detectors, and alarms to monitor and alert for any unauthorized access, security breaches, or equipment failures. The need for an alarm system may vary based on the security requirements and the importance of protecting the FM radio station's assets.
- Backup Power Generator: A backup power generator provides electrical power during extended power outages. It ensures the continuous operation of critical equipment, including transmitters and automation systems. The need for a backup power generator depends on factors such as the power availability, reliability of the primary power source, and the level of redundancy required for uninterrupted operation.
4. Parts & Accessories
- Antenna Mounting Parts (brackets, clamps, etc.): Antenna mounting parts, such as brackets and clamps, are used to securely attach the FM antenna to the tower or mast. The specific requirements for antenna mounting parts may vary based on factors such as the antenna type, size, weight, and installation location. While these parts are generally necessary for all FM radio stations, the exact specifications and configurations can differ depending on the equipment and installation requirements.
- Coaxial Connectors (N-type, BNC, etc.): Coaxial connectors are used to establish connections between coaxial cables, antennas, and other RF equipment. The choice of coaxial connectors may depend on the specific equipment used. Different FM radio stations may require different types of coaxial connectors based on their equipment compatibility and frequency range.
- Adapters and Couplers: Adapters and couplers are used to convert or connect different types of RF connectors or cables. They allow for flexibility in connecting various equipment with different connector types. The specific requirements for adapters and couplers may vary depending on the equipment and connections needed in the FM radio station setup.
- Cable Management System: A cable management system helps organize and manage the cables within the FM radio station setup. It includes cable trays, ties, clips, and other accessories to ensure a neat and organized installation. The specific requirements for cable management systems may depend on the size of the station, the number of cables, and the desired level of organization.
- RDS Encoder: An RDS (Radio Data System) encoder is responsible for encoding additional information such as station name, song title, traffic alerts, and other data into the FM signal. The RDS encoder requirements also remain consistent across different power levels.
- RF Filters: RF filters are used to eliminate unwanted signals or interference in the FM radio station setup. They help to improve signal quality and reduce noise. The specific requirements for RF filters may vary based on the desired frequency range, interference sources, and the level of filtering needed.
- Patch Panels: Patch panels are used to organize and connect multiple audio or RF signals to various equipment within the FM radio station setup. They provide flexibility in routing signals and allow for easy reconfiguration. The specific requirements for patch panels may depend on the number of signals and equipment connections required in the station.
- Cooling Fans: Cooling fans are used to dissipate heat generated by the FM radio station equipment, such as transmitters, amplifiers, or servers. They help maintain optimal operating temperatures and prevent overheating. The specific requirements for cooling fans may vary based on the power level and heat dissipation requirements of the equipment.
- Test and Measurement Equipment (spectrum analyzer, power meter, etc.): Test and measurement equipment, such as spectrum analyzers, power meters, and other tools, are used for monitoring, analyzing, and maintaining the FM radio station equipment. They assist in ensuring proper signal quality, power levels, and adherence to broadcasting regulations. While the specific equipment needs may vary, test and measurement tools are essential for all FM radio stations to maintain optimal performance and compliance.
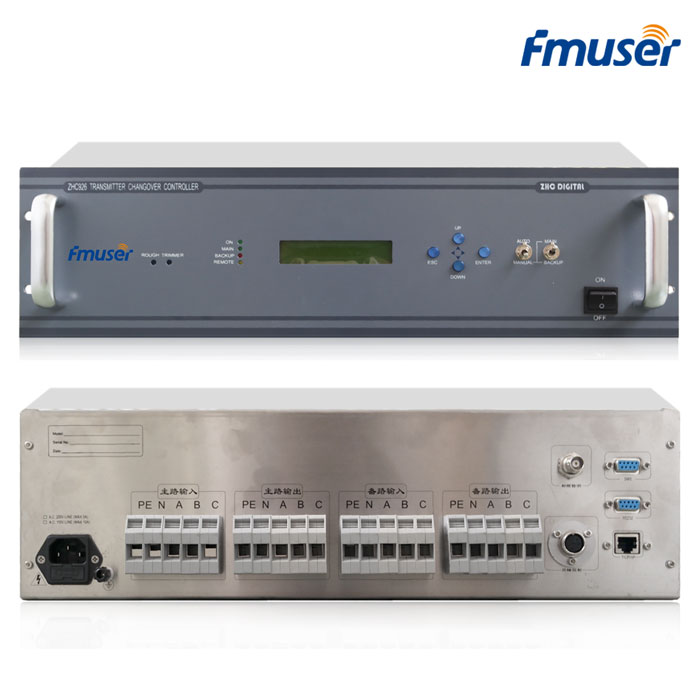
5. N+1 Solution
- Backup Transmitter: A backup transmitter is an additional transmitter that serves as a spare in case of primary transmitter failure. It ensures uninterrupted broadcasting by quickly replacing the primary transmitter. While backup transmitters are essential for high-power FM radio stations to minimize downtime, they may be optional for low-power or medium-power FM stations where the impact of downtime is relatively lower.
- Backup Exciter: A backup exciter is a spare unit that provides modulation and frequency stability for the FM signal. It serves as a backup in case the primary exciter fails. Backup exciters are typically used in high-power FM radio stations to ensure continuous operation. For low-power or medium-power FM stations, backup exciters may be optional depending on the desired level of redundancy and the availability of spare units.
- Automatic Switching System: An automatic switching system monitors the primary transmitter/exciter and automatically switches to the backup unit in case of failure. It ensures seamless transition and uninterrupted broadcasting. Automatic switching systems are commonly used in high-power FM radio stations to minimize downtime. For low-power or medium-power FM stations, the use of automatic switching systems may be optional depending on the desired level of automation and redundancy.
- Redundant Power Supplies: Redundant power supplies provide backup power to critical equipment such as transmitters, exciters, or control systems. They ensure continuous operation in the event of a primary power supply failure. Redundant power supplies are often used in high-power FM radio stations to minimize downtime and protect against power disruptions. The use of redundant power supplies may be optional for low-power or medium-power FM stations depending on the criticality of continuous operation and the availability of backup power sources.
- Redundant Audio Sources: Redundant audio sources refer to backup audio playback systems that ensure continuous audio content in case of failure or interruption in the primary audio source. Redundant audio sources are commonly used in FM radio stations to prevent dead air and maintain uninterrupted broadcasting. The use of redundant audio sources may depend on the desired level of redundancy and the criticality of continuous audio content delivery.
6. FM Combiner System
- FM Combiner: An FM combiner is a device used to combine the output signals from multiple FM transmitters into a single output, which is then connected to the FM antenna. It ensures efficient sharing of the antenna infrastructure. FM combiners are commonly used in situations where multiple transmitters need to operate on the same frequency or in close proximity. The combiner specifications depend on factors such as the number of transmitters, power levels, frequency range, and desired performance characteristics.
- Combiner Filters: Combiner filters are used in FM combiner systems to prevent interference between the combined signals. They help maintain signal purity and eliminate unwanted spurious emissions. Combiner filters are designed to attenuate out-of-band signals and harmonics while allowing the desired FM signal to pass through. The specific requirements for combiner filters depend on the frequency range, adjacent channel rejection, and filtering characteristics required for the FM system.
- Combiner Monitoring System: A combiner monitoring system is used to monitor the performance and health of the FM combiner system. It typically includes monitoring devices, sensors, and software that measure parameters such as power levels, VSWR (Voltage Standing Wave Ratio), and temperature. The monitoring system provides real-time data to ensure optimal performance, detect faults or failures, and facilitate maintenance and troubleshooting.
- Dividers: Dividers, also known as power dividers or splitters, are used in FM combiner systems to split the signal power from one input into multiple outputs. Dividers help distribute the power equally between multiple transmitters connected to the combiner. The specific requirements for dividers depend on the number of output ports, power levels, and impedance matching needed for the FM combiner system.
- Couplers: Couplers are passive devices used in FM combiner systems to enable signal coupling or splitting. They allow for the extraction or injection of a portion of the signal power while maintaining impedance matching and signal integrity. Couplers can be used for various purposes, such as signal monitoring, sampling, or feeding auxiliary equipment. The specific requirements for couplers depend on the power levels, frequency range, coupling ratio, and insertion loss specifications required for the FM combiner system.
7. FM Cavity System
- FM Cavities: FM cavities, also known as resonant cavities, are devices used in FM radio systems to filter and shape the frequency response of the transmitted signal. They are typically constructed as metallic enclosures with resonant elements inside, designed to resonate at the desired FM frequency. FM cavities are used to improve signal purity, attenuate out-of-band emissions, and enhance the selectivity of the transmitted signal. The specifications of FM cavities include the resonant frequency, bandwidth, insertion loss, and power handling capabilities.
- Cavity Filters: Cavity filters are specialized filters that use multiple resonant cavities to achieve high selectivity and attenuation of unwanted signals within the FM frequency range. They are designed to pass the desired FM signal while rejecting interfering signals outside the desired frequency band. Cavity filters are used in FM radio systems to improve signal quality, reduce interference, and meet regulatory requirements. The specifications of cavity filters include the center frequency, bandwidth, insertion loss, rejection levels, and power handling capabilities.
- Cavity Tuning System: A cavity tuning system is used to adjust the resonant frequency and bandwidth of the FM cavities. It allows for precise tuning and optimization of the cavities to match the desired frequency band and achieve optimal performance. The cavity tuning system includes tools and devices, such as tuning rods, variable capacitors, or tuning stubs, that are used to tune and adjust the resonant cavities to the desired frequency with high accuracy.
8. SFN (Single Frequency Network) Network
- SFN Transmitter: An SFN transmitter is a transmitter that is designed to operate in a Single Frequency Network (SFN). SFN involves the synchronized operation of multiple transmitters, all transmitting the same signal on the same frequency. The SFN transmitters are synchronized to ensure that the signal from each transmitter arrives simultaneously at the receiver, reducing interference and improving coverage. SFN transmitters typically have specific synchronization capabilities and are configured to work in conjunction with other transmitters in the SFN network.
- GPS Synchronization System: A GPS synchronization system is used in SFN networks to ensure precise synchronization between different transmitters. GPS receivers are used to receive signals from GPS satellites, allowing the SFN transmitters to synchronize their transmission timing accurately. The GPS synchronization system helps to synchronize the transmitters' clocks, ensuring that they transmit the signal in perfect alignment. This synchronization is crucial for maintaining coherence and reducing interference in the SFN network.
- SFN Monitoring System: An SFN monitoring system is used to monitor and analyze the performance of the SFN network. It typically includes monitoring devices, sensors, and software that measure parameters such as the signal strength, signal quality, and synchronization status at various locations within the SFN coverage area. The SFN monitoring system provides real-time data to ensure optimal performance, detect faults or synchronization issues, and facilitate maintenance and troubleshooting.
- SFN Switching System: An SFN switching system is used to control the switching between different transmitters in the SFN network. It ensures that the appropriate transmitter is active based on the coverage area and receiver's location. The SFN switching system automatically determines the best transmitter to use based on factors such as signal strength, signal quality, and synchronization status. The switching system helps to maintain seamless coverage within the SFN network and optimize the reception experience for the listeners.
9. FM Coupler System
- FM Couplers: FM couplers are devices used in FM radio systems to couple or split the FM signal power. They allow for the extraction or injection of a portion of the FM signal while maintaining impedance matching and signal integrity. FM couplers can be used for various purposes, such as signal monitoring, sampling, or feeding auxiliary equipment. The specifications of FM couplers include the power handling capabilities, coupling ratios, insertion loss, and frequency response.
- Coupler Monitoring System: A coupler monitoring system is used to monitor the performance and health of the FM coupler system. It typically includes monitoring devices, sensors, and software that measure parameters such as power levels, VSWR (Voltage Standing Wave Ratio), and temperature. The monitoring system provides real-time data to ensure optimal performance, detect faults or failures, and facilitate maintenance and troubleshooting specific to the coupler system.
- Coupler Filters: Coupler filters are used in FM coupler systems to shape the frequency response and attenuate unwanted signals or interference. They help maintain signal purity and eliminate spurious emissions. Coupler filters are designed to pass the desired FM signal while rejecting interfering signals outside the desired frequency band. The specifications of coupler filters include the center frequency, bandwidth, insertion loss, rejection levels, and power handling capabilities.
- Coupler Tuning System: A coupler tuning system is used to adjust the performance of the FM couplers, such as optimizing the coupling ratio, insertion loss, or return loss. It allows for precise tuning and adjustment of the couplers to match the desired coupling or splitting requirements. The coupler tuning system includes tools and devices, such as tuning rods or variable capacitors, that are used to tune and adjust the couplers for optimal performance and impedance matching.
Recommended FM Radio Station Package for You:
|
50W FM Radio Station Package |
150W FM Radio Station Package |
 |
 |
|
|
|
1000W FM Radio Station Package - Low Cost |
1000W FM Radio Station Package - Pro |
 |
 |
III. Complete FM radio studio equipment list
FM radio studio equipment comprises a range of essential tools that enable radio professionals to create captivating audio content for broadcasting. These equipment items form the backbone of a radio station's production capabilities, allowing for the capture, editing, and enhancement of sounds. With the right equipment, radio professionals can ensure the creation of high-quality and compelling audio that engages listeners.
The separation of FM radio studio equipment into different categories allows for flexible customization based on budget considerations. Broadcasters with lower budgets may prioritize functionality and practicality, focusing on the basic equipment needed for operation, while those with higher budgets may gravitate towards specific brands and extra functions to meet their advanced requirements.
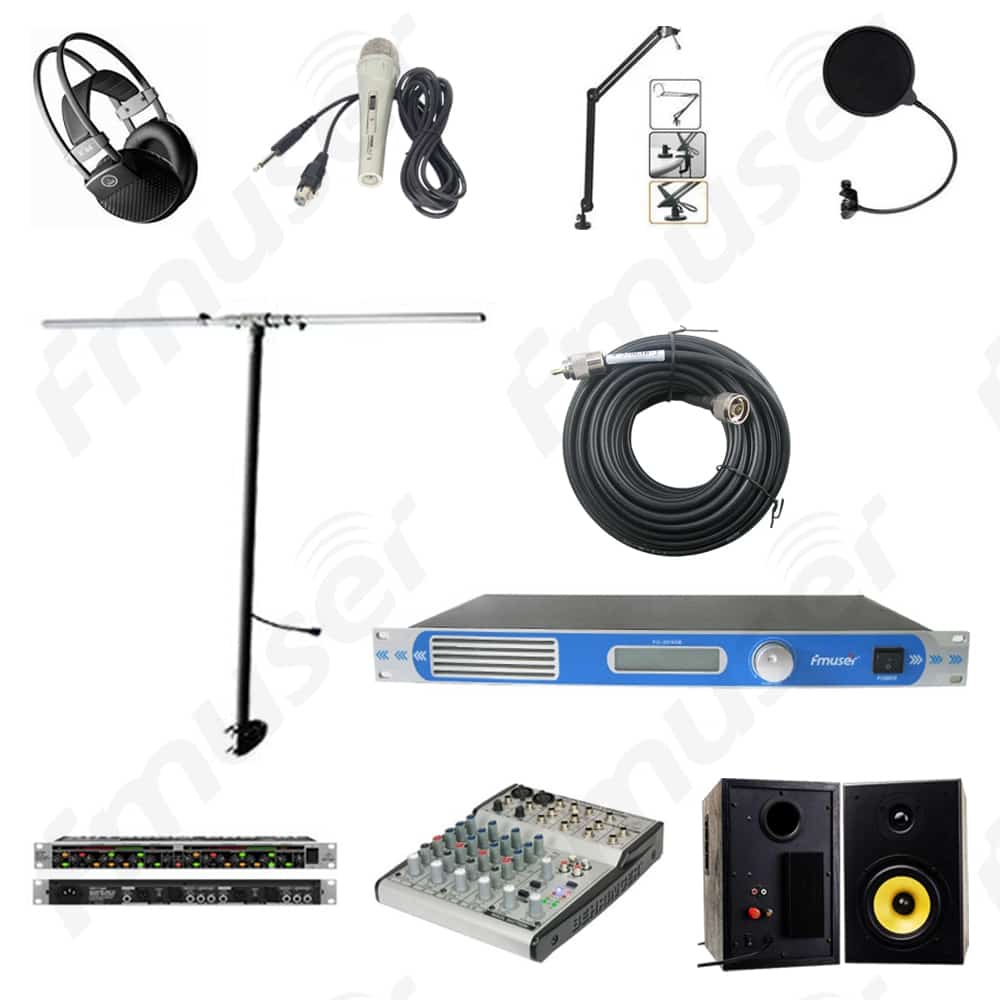
1. Very Basic FM Radio Studio Equipment List
Here's an extremely basic equipment list for an FM radio studio:
- Microphone: Microphones are vital tools for capturing sound with clarity and precision. Different types of microphones, such as dynamic, condenser, or ribbon microphones, offer varying characteristics suited for different applications in the studio.
- Audio Mixer: An audio mixer, or soundboard, allows for precise control and adjustment of audio signals from various sources. It enables the blending of different audio inputs, ensuring a well-balanced and polished audio mix.
- Headphones: High-quality headphones are essential for accurate audio monitoring. They enable radio professionals to critically assess audio quality, detect imperfections, and make precise adjustments during recording, editing, and mixing processes.
Eestimated Cost: $180 to $550 (even lower)
These very basic FM radio studio equipment setups are commonly utilized by individuals or organizations with limited budgets, such as community or small-scale radio stations, hobbyist broadcasters, or individuals getting started in radio production. These setups offer essential functionality and affordability, making them suitable for those who prioritize simplicity and cost-effectiveness in their broadcasting endeavors.
2. Standard FM Radio Studio Equipment List
Got more budget? Check this list for standard FM radio studio equipment list:
- High-quality Microphones: With a higher budget, you can invest in microphones that offer better audio capture and enhanced sensitivity. These high-quality microphones provide clearer sound reproduction, reduced background noise, and improved overall performance compared to basic microphones.
- Feature-rich Audio Mixer: A feature-rich audio mixer offers more advanced functionalities such as additional input channels, built-in effects processors, and more precise control over audio settings. This allows for more flexibility in mixing and producing audio content, resulting in a more polished and professional sound.
- Professional-grade Headphones: Professional-grade headphones provide superior sound accuracy, comfort, and durability. They offer better audio clarity, wider frequency response, and improved noise isolation, allowing for more accurate monitoring and assessment of audio quality.
- Advanced Audio Processor: An advanced audio processor offers a broader range of features and controls, including multi-band compression, advanced equalization options, and more precise audio shaping capabilities. This enables radio professionals to achieve a higher level of audio enhancement and optimization compared to basic audio processors.
- Studio Monitor Speakers: Studio monitor speakers with enhanced audio fidelity provide a more accurate and detailed representation of audio content. They offer improved frequency response, wider dynamic range, and better overall sound reproduction, allowing for more critical monitoring and audio evaluation.
- Adjustable and durable Microphone Stands: Adjustable and durable microphone stands offer greater flexibility in positioning microphones for optimal sound capture. They provide improved stability, adjustable height options, and enhanced durability compared to basic stands, ensuring precise microphone placement and longevity.
- Additional Cue Speakers: Additional cue speakers with improved audio quality deliver enhanced sound reproduction for hosts and producers to monitor content. These speakers offer better audio fidelity, wider frequency response, and improved overall clarity compared to basic cue speakers, allowing for more accurate content evaluation.
- Protective BOP Covers for specific equipment: Protective BOP (Broadcasting Operations Panel) covers are tailored to fit specific equipment, providing added protection against dust, spills, and accidental damage. These covers ensure the longevity and proper functioning of equipment, maintaining optimal performance and reducing the risk of issues due to environmental factors.
- Professional-grade On-Air Light: Professional-grade on-air lights offer enhanced features such as adjustable brightness, remote control capabilities, and customizable signaling options. They provide a more visually prominent indication of when the studio is live or when a broadcast is in progress, ensuring smoother on-air transitions and minimizing interruptions.
Eestimated Cost: $1,000 to $2,500 (even lower)
Standard FM radio studio equipment, offering a balance between affordability and enhanced features, is typically utilized by individuals or organizations with a moderate budget, such as independent radio stations, small broadcasting companies, podcasters, or content creators who prioritize higher quality audio production. These standard equipment options provide an upgrade from basic setups, allowing users to achieve a more polished and professional result in their FM radio broadcasting and production endeavors.
3. Luxury FM Radio Studio Equipment List
High-end Studio Microphones: High-end studio microphones offer exceptional audio capture quality, with advanced features such as extended frequency response, low self-noise, and superior sensitivity. They provide professional-grade sound reproduction and precise vocal or instrument recording, ensuring the highest level of audio clarity and fidelity.
- Premium Audio Mixer: A premium audio mixer boasts advanced features like high-resolution audio processing, extensive routing options, and intuitive control interfaces. They offer superior sound shaping capabilities, precise signal control, and enhanced audio clarity compared to basic or standard mixers, allowing for a more nuanced and professional mixing experience.
- Professional Studio Headphones: Professional studio headphones deliver unparalleled audio accuracy, extended frequency response, and superb isolation. With exceptional sound reproduction and heightened comfort, they enable detailed monitoring and critical evaluation of audio content, ensuring the utmost precision and accuracy in production.
- Advanced Audio Processor: Advanced audio processors offer a wide range of sophisticated features, including multi-band compression, detailed equalization control, advanced noise reduction algorithms, and precise audio enhancement tools. They provide unparalleled control over audio dynamics and quality, resulting in a professional-grade sound output that surpasses the capabilities of basic or standard processors.
- Studio Monitor Speakers with exceptional audio fidelity: Studio monitor speakers with exceptional audio fidelity offer pristine sound reproduction, accurate frequency response, and exceptional imaging capabilities. They provide an immersive listening experience, allowing producers and engineers to detect even the most subtle nuances in audio, ensuring the highest level of audio precision and quality.
- High-quality Microphone Stands and accessories: High-quality microphone stands provide superior stability, adjustable height options, and advanced shock absorption to reduce handling noise. They ensure precise microphone positioning and offer enhanced durability compared to basic or standard stands, contributing to a professional and reliable recording setup.
- Custom-built Cue Speakers with top-notch audio quality: Custom-built cue speakers are meticulously designed to provide unparalleled audio quality, precise sound imaging, and exceptional clarity for hosts and producers to monitor content. They offer superior audio fidelity compared to basic or standard cue speakers, enabling accurate content evaluation during live broadcasts or recording sessions.
- Customized BOP Covers for premium protection: Customized BOP (Broadcasting Operations Panel) covers provide a tailored fit and supreme protection for specific equipment. They are designed with top-quality materials to shield against dust, spills, and accidental damage, ensuring the longevity and optimal performance of the equipment.
- State-of-the-art On-Air Light: State-of-the-art on-air lights offer advanced features such as adjustable brightness, customizable signaling options, and remote control capabilities. They provide a visually prominent indication of when the studio is live or when a broadcast is in progress, ensuring seamless on-air transitions and minimizing interruptions.
- Cutting-edge Button Panel and control system: A cutting-edge button panel and control system offer extensive programmability, precise tactile feedback, and advanced integration options. They provide broadcasters with comprehensive control over various audio elements, facilitating smooth and efficient operation during live broadcasts or production sessions.
- High-end Phone Talkback System: High-end phone talkback systems provide exceptional audio quality, advanced communication features, and seamless integration with other studio equipment. They offer crystal-clear communication between radio hosts and callers, ensuring clear and professional conversation during live call-in segments.
- Top-tier Talent Panel: Top-tier talent panels offer advanced features such as flexible microphone controls, extensive connectivity options, and intuitive user interfaces. They provide radio hosts and guests with professional-grade interface and control, enhancing their performance and providing seamless interaction within the studio environment.
- Broadcast Workstation: A broadcast workstation with specialized software provides comprehensive production tools, automation control, and seamless integration with various studio equipment. It offers advanced functionality for audio editing, scheduling, playout, and streamlining workflows, enhancing the efficiency and professionalism of the broadcasting process.
- Comprehensive Sound Effects Libraries: Comprehensive sound effects libraries offer an extensive collection of high-quality sound effects, jingles, and music beds to enhance radio productions. They provide broadcasters with a vast array of options for creative audio enhancements, enabling them to create engaging and dynamic content.
- High-quality Recording Devices: High-quality recording devices offer advanced recording capabilities, higher sample rates, expanded storage capacity, and superior audio fidelity compared to basic or standard devices. They ensure pristine audio capture and reliable storage for professional-grade recordings, providing broadcasters with uncompromising quality.
- Custom-designed Furniture: Custom-designed furniture, such as podcast tables, studio tables, and chairs with custom features, offers a tailored and ergonomic studio setup. They provide enhanced comfort, optimized workflow, and aesthetic appeal, allowing broadcasters to create a luxurious and professional environment.
- Sound Insulation Cotton for effective soundproofing and acoustic treatment: Sound insulation cotton, also known as acoustic panels, plays a vital role in soundproofing and acoustic treatment of the studio space. It effectively absorbs unwanted echoes, reduces background noise, and enhances sound clarity, optimizing the acoustics for professional-grade audio production.
Eestimated Cost: $10,000 to $50,000 or even higher
Luxurious and professional equipment options are typically utilized by established radio stations, high-budget broadcasting companies, professional broadcasters, production studios, and those who prioritize top-tier audio quality, advanced features, and a prestigious broadcasting environment. These equipment choices cater to individuals and organizations seeking the utmost in audio excellence and premium broadcasting capabilities, allowing them to deliver an unparalleled radio experience to their audience.
IV. Where to Buy the Best Radio Station Equipment?
Looking to build a complete FM radio station? FMUSER is your one-stop solution, offering a wide range of products and services to meet all your requirements, regardless of whether you need low power, medium power, or high power equipment. Our comprehensive offerings cover both hardware and software aspects, ensuring a turnkey solution for your radio station setup.
- Wide Range of Products: FMUSER provides an extensive selection of FM broadcast equipment, including FM transmitters, antennas, audio processors, mixers, cables, and more. Our products cater to various power levels, accommodating low power community stations, medium power regional broadcasters, and high power metropolitan radio stations.
- Turnkey Solutions: We go beyond providing equipment. FMUSER offers turnkey solutions that encompass the design and setup of your radio station. We provide expert guidance in designing radio studios and transmission rooms, ensuring optimal layout, acoustics, and equipment placement for seamless operations.
- Designing Services: Our team of experienced professionals can assist you in designing a custom radio studio and transmission room tailored to your specific needs. We consider factors such as workflow, equipment integration, soundproofing, and ergonomics to create an efficient and professional environment.
- On-Site Installation Services: FMUSER offers on-site installation services to ensure the proper setup and configuration of your FM broadcast equipment. Our skilled technicians will visit your location, install the equipment, and perform comprehensive testing to guarantee smooth operation and optimal performance.
- Technical Support and Training: We are committed to providing exceptional customer support. FMUSER offers technical assistance and training to help you maximize the potential of your radio station setup. Our team is available to answer your questions and provide guidance both during the installation process and for ongoing operations.
FMUSER's strength lies in our ability to offer a comprehensive solution for building an FM radio station. With our wide range of products, turnkey solutions, designing services, on-site installation support, and software offerings, we provide the expertise and support required to ensure the success of your radio station venture. Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements and let FMUSER be your trusted partner in building a professional FM radio station.
V. Conclusion
On this page, we learn various types of radio station equipment and how they work together. Do you need to buy the best radio station equipment for providing broadcasting services? You'll find that all the equipment you need is available on FMUSER's website at the best prices. Contact us right now!
Tags
Contents
Related Articles
CONTACT US

FMUSER INTERNATIONAL GROUP LIMITED.
We are always providing our customers with reliable products and considerate services.
If you would like to keep touch with us directly, please go to contact us