Coax Connectors
RF cable connectors are critical components in industries like telecommunications, aerospace, and broadcasting, ensuring seamless signal transmission. At FMUSER, we specialize in high-performance RF connectivity solutions tailored for professionals navigating complex network setups.
1. Precision Connectivity Solutions for Modern Demands
Our classification system simplifies selection by categorizing products based on power handling, frequency range, and application-specific needs. Whether you’re upgrading 5G infrastructure or deploying IoT systems, our connectors streamline your workflow with precision engineering.
2. Built to Last: Industrial-Grade Performance & Innovation
FMUSER’s RF cable connectors combine military-grade durability, low-loss signal efficiency, and CE/RoHS certifications for global compliance. Advanced features like triple-shielded insulation and gold-plated contacts maximize signal integrity, even in harsh environments. Scalable from compact IoT devices to high-power broadcast systems, our connectors cater to hobbyists, enterprises, and defense integrators alike.
3. Transformative Applications of FMUSER’s RF Cable Connectors
- 5G/6G Telecom Systems: Our low-loss N-type connectors ensure high-speed data transfer with minimal interference, critical for ultra-reliable 5G base stations.
- Satellite & Aerospace Communications: SMA connectors with vibration resistance guarantee uninterrupted links in flight systems and satellite payloads.
- Medical Imaging Equipment: High-frequency BNC connectors enable crystal-clear signal transmission for MRI and ultrasound diagnostics.
- Broadcast & Live Streaming: Weatherproof UHF connectors support 4K video streaming in outdoor broadcast setups.
4. Why FMUSER Stands Out: Factory to Field, Faster & Smarter
- Direct Factory Pricing: Save 30-50% with no middlemen.
- Same-Day Global Shipping: Always stocked for urgent projects.
- Turnkey Integration: Pre-configured kits with antennas, cables, and connectors.
- OEM Customization: Modify impedance, plating, or housing materials for unique needs.
- On-Site Support: Global technicians for installation and troubleshooting.
Trusted in over 90 countries, our solutions power networks from smart cities to military radar systems.
5. Your RF Connector Buying Checklist
Evaluate frequency range (DC-40 GHz), impedance (50Ω/75Ω), IP rating (up to IP68), and connector type (SMA, BNC, N). Match these to your project’s bandwidth requirements, environmental challenges, and budget, ensuring seamless integration with existing antennas or transmitters.
-
![FMUSER L29-J Male 7/16 Din to IF110 3-1/8" EIA Flange Connector Adaptor]()
FMUSER L29-J Male 7/16 Din to IF110 3-1/8" EIA Flange Connector Adaptor
Price(USD):Ask for a quotation
Sold:49
-
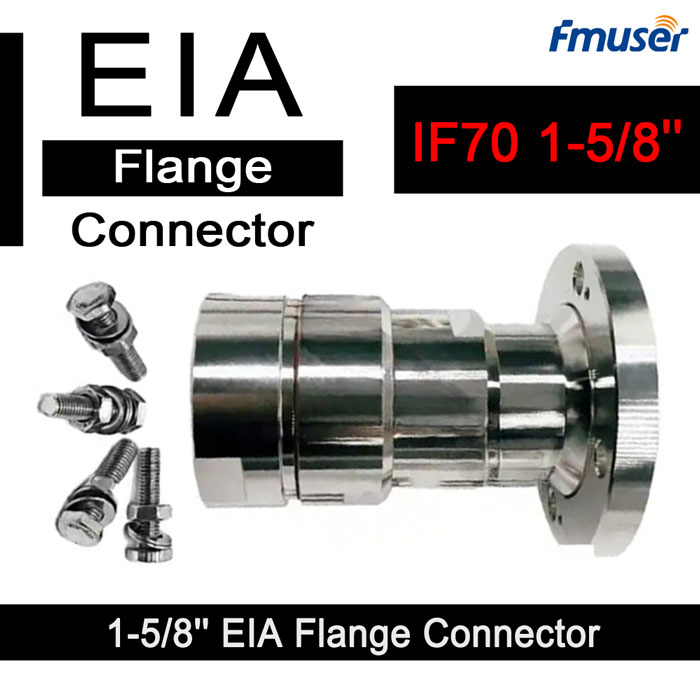
![FMUSER L29-J Male 7/16 Din to IF70 1-5/8" EIA Flange Connector Adaptor]()
FMUSER L29-J Male 7/16 Din to IF70 1-5/8" EIA Flange Connector Adaptor
Price(USD):Ask for a quotation
Sold:211
-
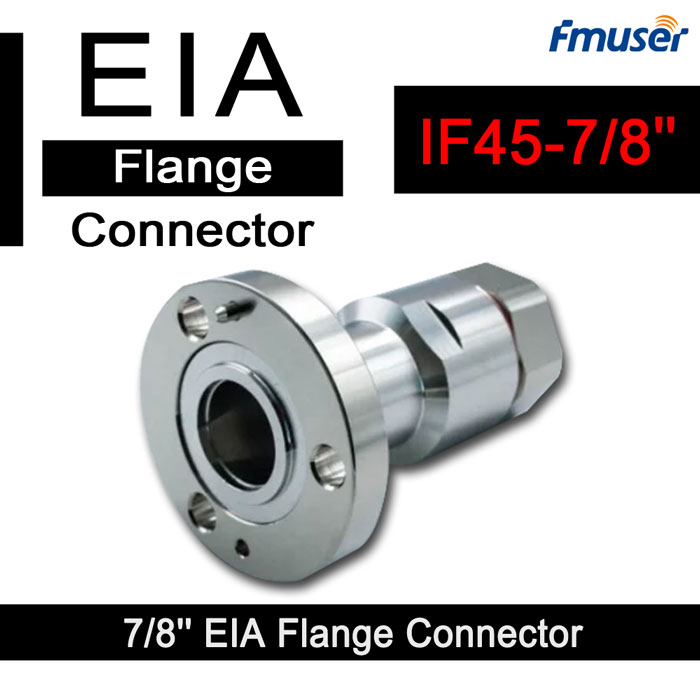
![FMUSER L29-J Male 7/16 Din to IF45 7/8" EIA Flange Adaptor]()
-
![FMUSER 7/16 Din to N Adapter L29-J Male to N Male]()
-
![FMUSER 1 2 Coax N-J (NM-1/2) N Male Connector for RF 1 2 Feeder Cable]()
FMUSER 1 2 Coax N-J (NM-1/2) N Male Connector for RF 1 2 Feeder Cable
Price(USD):Ask for a quotation
Sold:841
-
![FMUSER 1 2 Coax N-K (L4TNF-PSA) N Female Connector for RF 1 2 Feeder Cable]()
FMUSER 1 2 Coax N-K (L4TNF-PSA) N Female Connector for RF 1 2 Feeder Cable
Price(USD):Ask for a quotation
Sold:841
-
![FMUSER L29K 7-16 DIN Female 1 2 Coax Connector DIN-K 1/2 DF-1/2 DINF-1/2 RF Coax Cable Connector for Feeder Cable]()
Price(USD):Ask for a quotation
Sold:1,846
-
![FMUSER L29K 7-16 (7/16) DIN Female 7 8 RF Connector DF-7/8 DINF-7/8 DIN-K 7/8 7 8 Feeder Cable Connector]()
Price(USD):Ask for a quotation
Sold:1,211
-
![FMUSER L29J 7/16 (7-16) DIN 1 2 Coax Connector L29M-1/2 DINM-1/2 RF Coax Cable Connector for Feeder Cable]()
Price(USD):Ask for a quotation
Sold:2,412
-
![FMUSER L29J 7-16 (7/16) DIN 7 8 Din Male Connector DM-7/8 DINM-7/8 RF Coax Cable Connector for Feeder Cable]()
Price(USD):Ask for a quotation
Sold:1,451
-
![FMUSER 3-1/8" IF110 Coax 3 1 8 EIA Flange Connector]()
-
![FMUSER 1 5/8" IF70 Coax 1 5 8 EIA Flange Connector Male to Female (J-type)]()
FMUSER 1 5/8" IF70 Coax 1 5 8 EIA Flange Connector Male to Female (J-type)
Price(USD):Ask for a quotation
Sold:2,578
-
![FMUSER 7/8" IF45 Coax 7 8 EIA Flange Connector Male to Female (J-type)]()
FMUSER 7/8" IF45 Coax 7 8 EIA Flange Connector Male to Female (J-type)
Price(USD):Ask for a quotation
Sold:1,568
- What are the applications of different tpyes of coax cable connectors?
- Different types of coaxial cable connectors have different applications and are installed differently based on the specific context in which they will be used. Here is an overview of some of the most common coaxial cable connectors, their applications, and how they are installed:
1. BNC (Bayonet Neill-Concelman) connectors: BNC connectors are commonly used in radio frequency and video applications, including FM broadcasting. They are popular because of their relatively low cost, ease of use, and quick-connect/disconnect mechanism. BNC connectors are installed by sliding the connector onto the coaxial cable, turning the bayonet mechanism until it clicks into place, and then screwing on the collar, pressing the shield against the connector and making a threaded connection through the outside ferrule. BNC connectors can be used with various types of coaxial cable, including RG-59 and RG-6.
2. N-type connectors: N-type connectors are popular for use in FM broadcasting applications because they provide good shielding and maintain a constant impedance across a wide frequency range. They are often used with higher-power transmitters and can handle frequencies up to 11 GHz. N-type connectors are typically threaded, requiring the coax to be threaded onto the male connector and tightened using a wrench. N-type connectors are often used with high-quality coaxial cables, like RG-213 or LMR-400.
3. SMA (Subminiature Version A) connectors: SMA connectors are used in a variety of applications, including FM broadcasting, wireless communications, and GPS. They are popular for use with equipment that requires a small, compact connector. SMA connectors are typically used with smaller coaxial cables like RG-174 or RG-58, and are attached by threading the connector onto the coaxial cable. SMA connectors are also available with a reverse-polarity design for use in wireless internet and cellular networks.
4. F-type connectors: F-type connectors are commonly used in cable television and satellite TV applications. They are also used in some FM broadcasting applications, such as for connecting the FM broadcasting transmitter's output to an omnidirectional antenna. F-type connectors are installed by twisting the connector onto the coaxial cable's threading. These connectors are typically suitable for use with RG-6 and RG-59 coaxial cables.
The choice of coaxial cable connector depends on the application, frequency range, power requirements, and desired performance. Generally, coaxial cable connectors are installed by sliding them onto the coaxial cable, and then securing them using a threaded or bayonet-type mechanism. A good quality coaxial cable connector installation will ensure low-loss connections, good shielding and grounding, and reliable signal transmission.
In summary, different types of coaxial cable connectors have different applications and installation requirements depending on the specific demands of FM broadcasting and other signal transmission applications. BNC, N-type, SMA, and F-type connectors are some of the most commonly used types of coaxial connectors in FM broadcasting. Choosing the right type of connector and correctly installing it is important for maintaining high-quality transmission and reducing the risk of interference or signal loss.
- Can coaxial cable connectors be applied with rigid transmission lines?
- Coaxial cable connectors can be used with rigid transmission lines, but certain types of coaxial connectors are specifically designed for use with rigid lines. Rigid transmission lines are typically used in high-power applications where the distances between the RF amplifier and antenna are relatively short, and where low-loss and high-power handling capabilities are required.
One popular type of connector used in rigid transmission lines is the N-type connector. N-type connectors are designed specifically for use with high-performance coaxial cables and rigid transmission lines. They are available in both 50 ohm and 75 ohm versions, making them suitable for use in a range of applications, including both FM broadcasting and other high-power RF applications.
Other types of coaxial connectors, such as BNC or SMA connectors, are not typically used in rigid transmission lines since they are not designed to handle the high power levels associated with these applications. Instead, connectors used with rigid transmission lines are typically rated for high voltage and high power applications, with more robust constructions and materials to withstand the rigors of high power transmission.
In summary, coaxial cable connectors can be used with rigid transmission lines, but only certain types of connectors are suitable for use in high-power and high-voltage applications. N-type connectors are a popular choice for use in rigid transmission lines, because of their robust construction, high power ratings, and low-loss connection to the transmission line. For FM broadcasting applications, selecting the appropriate type of connector for the specific application is critical to optimizing performance and reliability.
- What are common types of coaxial cable connector and their differences?
- There are several types of coaxial cable connectors commonly used in radio broadcasting. Here are some of the most common types and their key features:
1. BNC (Bayonet Neill-Concelman): This is a type of quick-connect RF connector that has a bayonet-style coupling mechanism. It is commonly used in broadcast applications due to its low cost and rugged construction. BNC connectors are relatively small, and are mainly used for transmission lines with a diameter of less than 0.5 inches.
2. N-Type: This is a threaded RF connector that is commonly used in applications requiring higher power levels, such as those used in television broadcasting. N-type connectors typically have a higher reliability and more secure connection compared to BNC connectors.
3. SMA (SubMiniature version A): This is a threaded RF connector that is commonly used in applications where size is a concern, such as in portable broadcast equipment. SMA connectors have excellent electrical properties, however, they are not designed for high power applications.
4. F-Type: This is a threaded RF connector that is commonly used in cable and satellite television applications. F-type connectors have a relatively low cost, and are easy to install, but they are not as reliable or durable as other connector types.
5. TNC (Threaded Neill-Concelman): This is a threaded RF connector that is commonly used in applications requiring high-frequency signals, such as in satellite communications or radar systems. TNC connectors are designed to withstand high temperatures and shocks, making them ideal for rugged environments.
In terms of advantages and disadvantages, each connector type has its own set of unique features. For example, BNC connectors are commonly used in broadcasting applications due to their low cost and rugged construction, while N-type connectors are often used in high power applications due to their higher reliability. SMA connectors are an ideal choice for portable broadcast equipment due to their small size, while F-type connectors are commonly used in cable and satellite television applications due to their low cost and ease of installation. TNC connectors are ideal for high-frequency applications due to their ability to withstand high temperatures and shocks.
The price of each connector type will vary depending on the manufacturer, but in general, BNC and F-type connectors tend to be the least expensive, while N-type and TNC connectors can be more expensive due to their higher reliability and durability.
The applications and corresponding coaxial cables or rigid transmission lines depend on the specific requirements of the broadcasting system. Coaxial cables are typically used for applications that require flexibility and ease of installation, such as for portable equipment. Rigid transmission lines, on the other hand, are often used in more permanent installations where stability is critical.
In terms of basic structure and configuration, all coaxial connectors consist of a male or female connector attached to the end of a coaxial cable or rigid transmission line. The male connector typically has a center pin that connects to the center conductor of the cable or transmission line, while the female connector has a socket that receives the center pin of the male connector.
Some connectors may have a flange or unflanged design, depending on the application. Unflanged connectors are typically used for applications where space is limited, while flanged connectors are used for applications where a more secure or stable connection is required.
Installation methods vary depending on the connector type and the specific requirements of the application. Some connectors may require a specialized crimping tool or other equipment for installation, while others can be installed using a simple wrench or pliers.
In terms of size and appearance, connector sizes can range from very small SMA connectors to very large N-type connectors. The appearance of the connector will depend on the manufacturer and the specific design of the connector, but all connectors will have some form of male and female connection points.
It's worth noting that when selecting a coaxial cable connector for radio broadcasting, it's important to ensure that the connector is compatible with the corresponding cable or transmission line. This includes ensuring that the connector has the correct impedance level, which is typically 50 ohms or 75 ohms for most broadcasting applications.
Additionally, it's important to consider the environmental conditions in which the connector will be used. For example, connectors used in outdoor broadcasting installations may need to be weather resistant, while connectors used in high-heat or high-moisture environments may need to be designed to withstand those conditions.
Overall, the type of coaxial cable connector used in a broadcasting installation will depend on a variety of factors, including the specific application requirements, the types of cables or transmission lines being used, and the environmental conditions in which the connectors will be installed. By carefully considering these factors and selecting the appropriate connector for each situation, broadcasters can ensure reliable and high-quality signal transmission in their installations.
- How to choose coaxial cable connector based on applications?
- When choosing a coaxial cable connector for broadcasting applications, it's important to consider several factors, including the required frequency range, the power levels involved, and the specific requirements of the application. Here are some general guidelines for choosing a connector in common broadcasting applications:
1. UHF broadcasting: UHF broadcasting typically requires connectors that can handle high-frequency signals, such as TNC or N-type connectors. These connectors have a higher frequency range and can handle higher power levels, making them ideal for UHF applications.
2. VHF broadcasting: VHF broadcasting typically operates at lower frequencies than UHF, and typically requires connectors that are capable of handling lower power levels. BNC connectors are often a good choice for VHF applications, as they can handle frequencies up to around 4 GHz and have a relatively low cost.
3. FM broadcasting: FM broadcasting typically requires connectors that are capable of handling higher power levels than VHF or UHF, as well as high-quality signals. N-type connectors are often a good choice for FM applications due to their high power handling capabilities and excellent signal quality.
4. AM broadcasting: AM broadcasting typically operates at even lower frequencies than FM, and requires connectors that can handle these lower frequencies. F-type connectors are often used in AM broadcasting applications, as they are capable of handling frequencies down to around 5 MHz and can be used with low-power transmissions.
5. TV broadcasting: TV broadcasting typically requires connectors that can handle a wide range of frequencies, as well as high power levels for some applications. BNC, N-type, and TNC connectors are all commonly used in TV broadcasting, depending on the specific requirements of the application.
It's important to note that these are just general guidelines, and the specific requirements of each broadcasting application may vary depending on factors such as the transmit power levels, antenna gain, and the surrounding environment. When selecting a coaxial cable connector for a broadcasting installation, it's important to carefully consider all of these factors and choose a connector that is appropriate for the specific requirements of the application.
- What are the structures of a coaxial cable connector?
- The structure of a coaxial cable connector can vary depending on the specific type and design of the connector, but in general, there are several common components that are found in most connectors. These include:
1. Connector Body: The connector body is the main structural component of the connector, and is typically made from a metal or plastic material. The body may be threaded or have a bayonet-style coupling mechanism, depending on the design of the connector.
2. Center Pin: The center pin is a metal conductor that extends from the center of the connector body, and is used to make contact with the center conductor of the coaxial cable. The center pin is typically held in place by a spring or other mechanism that provides a secure electrical connection.
3. Dielectric Insulator: The dielectric insulator is a non-conductive material that surrounds the center pin and separates it from the outer conductor of the coaxial cable. The insulator is typically a rigid or flexible plastic material that helps to maintain the electrical properties of the connector.
4. Outer Conductor: The outer conductor surrounds the dielectric insulator and provides a shield against electromagnetic interference. The outer conductor is typically made from a metal material, such as copper or aluminum, and may be designed as a single solid piece or as a series of interconnected pieces.
5. Gasket or O-Ring: The gasket or O-ring is used to create a weather-tight seal between the connector and the coaxial cable or transmission line. The gasket is usually made from a rubber or plastic material and is designed to withstand a range of environmental conditions.
6. Coupling Nut: The coupling nut is used to attach the connector to the coaxial cable or transmission line, and provides a secure mechanical connection. The coupling nut is typically threaded and may be designed as a one-piece or multi-piece component, depending on the specific connector design.
When these components are assembled, they form a complete coaxial cable connector that can be used to connect coaxial cables or transmission lines in a variety of applications.
- How to correctly install a coaxial cable connector?
- Installing a coaxial cable connector on a radio broadcasting antenna requires a few steps to ensure a reliable connection. Here's a general process for installation:
1. Choose the right connector: Select a connector that is compatible with the type of coaxial cable you will be using, with the required frequency range and power handling capacity for the antenna and transmitter.
2. Prepare the cable: Strip back the outer jacket of the coaxial cable to expose the inner conductor and dielectric insulator. Trim the dielectric to the correct length based on the connector specifications.
3. Install the connector: Carefully thread the connector over the prepared coaxial cable, in accordance with the manufacturer's instructions. Assemble the connector and thread on the coupling nut to secure it in place.
4. Terminate the cable: Solder or crimp the center pin connector onto the inner conductor, ensuring that it makes good electrical contact. Attach the outer conductor to the connector body, using the crimp ring provided with the connector.
5. Attach the antenna and transmitter: Connect the other end of the coaxial cable to the antenna and transmitter. Ensure that the antenna is grounded and that all connections are secure.
6. Test the installation: Use a cable tester to ensure that there are no shorts or open circuits in the installation. Check the transmission signal quality to ensure that the antenna is properly connected and functioning correctly.
When installing a coaxial cable connector on a radio broadcasting antenna, there are a few things to keep in mind:
- Work carefully when stripping and preparing the coaxial cable, to avoid damaging the inner conductor or dielectric.
- Follow the manufacturer's instructions carefully when installing the coaxial cable connector, to ensure that you're using the correct procedure for the given connector.
- Use caution and appropriate safety measures when working with transmission equipment, as high voltages and power levels can present a hazard.
- Test the installation carefully before putting the antenna into service, to ensure that it is working correctly and providing a reliable signal.
- What are the most important specifications of an coaxial cable connector
- The most important physical and RF specifications of a coaxial cable connector include:
1. Impedance: The impedance of the connector should match that of the cable and other components in the signal path. Typically, coaxial cable connectors have an impedance of 50 or 75 ohms.
2. Frequency Range: The frequency range specifies the maximum frequency that the connector can transmit without significant signal degradation. This is an important spec, especially for high-frequency applications such as radio broadcasting.
3. Power Handling: The maximum power that the connector can handle without causing damage or signal loss is another critical spec. It's essential to ensure the connector's power handling capacity is sufficient for the transmitter's output power, so as not to cause damage or degrade the signal.
4. Connector Type: There are several different types of coaxial connectors available, including BNC, SMA, N-Type, and TNC. The connector type affects the frequency range, power handling, and physical dimensions, making it essential to match the connector to the application.
5. Insertion Loss: The insertion loss of a connector is the amount of signal loss that occurs due to the connector's insertion into the signal path. The lower the insertion loss, the better the signal transfer efficiency.
6. Voltage Standing Wave Ratio (VSWR): The VSWR is a measure of the signal reflection that occurs due to the impedance mismatch between the connector and the antenna or transmission line. A high VSWR can lead to signal degradation or damage to the signal source.
7. Operating Environment: The environment in which the cabling will be used should be considered when choosing a connector. For example, if the cabling will be used in a harsh outdoor environment, a heavy-duty, weather-resistant connector would be appropriate.
In summary, the physical and RF specifications of a coaxial cable connector are critical to ensuring the proper transmission of an RF signal. These specs include impedance, frequency range, power handling, connector type, insertion loss, and VSWR. It's essential to select a connector with the appropriate specifications for the particular application and system to ensure optimal performance and reliable transmission of the broadcast signal.
In general, the type of coaxial cable and the transmitter’s connector type are the most critical factors to consider when choosing a coaxial cable connector. For best results, purchase connectors that are designed to work with the specific type of coaxial cable you are using, and choose a connector that is compatible with your transmitter’s connector type.
It’s also important to consider the operating environment and frequency range, as these factors can play a role in the performance and reliability of the signal transmission. Using a mismatched connector or an incompatible connector type can lead to signal loss, degradation, or complete failure, so it’s crucial to choose correctly.
- What are common components that consists of a broadcast antenna system?
- A radio broadcasting antenna system consists of several components and equipment, including:
1. Antenna: The antenna is the main component of a radio broadcasting system used to transmit or receive signals. It's designed to radiate electromagnetic waves into the surrounding space. The coaxial cable connector provides the connection between the antenna and the transmission line.
2. Transmission Line: The transmission line carries the signal from the transmitter to the antenna and vice versa. It's designed to minimize transmission loss and impedance mismatch that can affect the signal quality. The coaxial cable connector provides a secure and reliable connection between the transmission line and the antenna.
3. Transmitter: The transmitter generates the radio frequency signal that's amplified and transmitted through the antenna. It's responsible for converting electric signals into electromagnetic signals that can be transmitted over the airwaves.
4. Receiver: The receiver is responsible for receiving the transmitted signals. It's used in radio broadcasting to receive different channels transmitted through various frequencies.
5. Coaxial Cable: The coaxial cable is a type of cable used to transmit high-frequency signals with low loss and minimal interference. The cable comprises a center conductor surrounded by insulation and a shield on the outside. The coaxial cable connector provides a connection point between the coaxial cable and the transmission line or antenna.
6. Coaxial Cable Connector: The coaxial cable connector is a device used to facilitate the connection between coaxial cable, transmission line, and antennas. It's designed to provide a secure and stable electrical connection, minimize transmission loss and interference, and ensure stable and optimal signal quality.
In summary, a radio broadcasting antenna system consists of several components and equipment that work together to transmit and receive radio signals. These components include the antenna, transmission line, transmitter, receiver, coaxial cable, and coaxial cable connector. The coaxial cable connector provides the critical function of facilitating a secure, reliable, and efficient connection between the various components of the broadcasting system, ensuring optimal performance and high-quality transmission of the broadcast signals.
- What are common materials to make a coaxial cable connector?
- Coaxial cable connectors can be made from a variety of materials depending on the application requirements and intended use. Here are some common materials used to make coaxial cable connectors:
1. Brass: Brass is a common material used in coaxial cable connectors due to its good conductivity, stable mechanical properties, and ease of machining.
2. Stainless Steel: Stainless steel is a popular material for coaxial cable connectors used in harsh or corrosive environments due to its excellent corrosion resistance, strength, and durability.
3. Aluminum: Aluminum is a lightweight material used in coaxial cable connectors where weight is a concern, such as in aerospace applications.
4. Zinc: Zinc is a low-cost material used in some coaxial cable connectors, primarily those intended for indoor or low-temperature environments.
5. Plastic: Some coaxial cable connector parts such as insulators and bodies are made of plastic. Plastic materials offer excellent insulation properties, flexibility, and lightweight.
6. Copper: Copper is used as a plating material for coaxial cable connectors due to its excellent electrical conductivity, corrosion resistance, and oxidation resistance.
In summary, coaxial cable connectors can be made from a range of materials depending on the application requirements. Brass, stainless steel, aluminum, zinc, plastic, and copper are all common materials used to make coaxial cable connectors. Choosing the proper material is essential to achieve optimal performance, reliability, and durability of the coaxial cable connector.
- What are common terminologies to coaxial cable connector?
- Here are some common terminologies related to coaxial cable connectors and their meanings:
1. Coaxial Connector Type: Coaxial connectors come in various types, such as BNC, SMA, N-Type, and TNC. The connector type specifies the physical interface of the connector and the frequency range and power handling it can support.
2. Gender: Coaxial connectors are either male or female. A male connector has a center pin that protrudes outward, while a female connector has a center receptacle that accepts the male pin.
3. Impedance: Impedance is the resistance to the flow of electrical energy in a circuit. Coaxial cable connectors are designed to work with specific impedance cables, usually either 50 or 75 ohms.
4. Frequency Range: The frequency range specifies the maximum frequency that the connector can transmit without significant signal degradation. Higher frequency connectors typically have a more precise mechanical interface, so the connector does not loosen due to vibration or other stressors.
5. Power Handling: The power handling capacity specifies the maximum amount of power a connector can transmit without degradation or damage.
6. Connector Series: Connector series refer to the design of the connector and the frequency range it can support. Examples of connector series include L-series and L29-K.
7. Connector Size: Connector size refers to the physical dimensions of the connector, typically based on thread size.
8. Flanged and Unflanged: Coaxial cable connectors can either be flanged or unflanged. Flanged connectors have a flat, circular flange on the connector body that secures the connector in place with a mounting nut. Unflanged connectors, on the other hand, don’t have a flange and are usually soldered directly onto the coaxial cable.
9. EIA Connector: EIA stands for “Electronic Industries Alliance,” which is a trade organization that sets standards for electronic equipment. An EIA connector is a type of RF connector that adheres to EIA standards for dimensions, impedance, and performance.
10. IF70, IF110, IF45: These numbers refer to the diameter of the connector, with IF70 having a diameter of 7.0 mm, IF110 having a diameter of 11.0 mm, and IF45 having a diameter of 4.5 mm. The larger the diameter of the connector, the higher the frequency range it can support.
11. DINF: DINF is a type of connector series designed for high-frequency applications, typically up to 12.4 GHz. It has an impedance of 50 ohms and consists of a threaded body that secures the connector in place.
12. L4TNF-PSA: L4TNF-PSA is a type of flanged connector designed for use with LMR-400 coaxial cable. It has a threaded body and an impedance of 50 ohms, and its power handling capacity is high.
13. DINM: DINM is a type of connector series that uses a threaded interface to secure the connector in place. It has an impedance of 50 ohms and supports a frequency range of up to 4 GHz.
For example, the term "7/16 DIN male connector" refers to a male coaxial cable connector that uses a 7/16 DIN interface, which has a frequency range of up to 7.5 GHz and is commonly used in high-power applications. It typically has a low VSWR and high power handling capability.
The term "L29-K connector" refers to a type of connector series designed for high-frequency applications up to 18 GHz, with an impedance of 50 ohms. The connector has a high-power handling capacity and is commonly used in communication and broadcasting systems.
Understanding these terms is necessary to ensure the proper selection of the connector for a specific application and reliable transmission of the signal.
- What differs a commercial and consumer-grade coaxial cable connector?
- The main differences between commercial and consumer-level coaxial cable connectors in radio broadcasting depend on several factors, including the types of coaxial cables used, advantages, disadvantages, prices, applications, performance, structures, frequencies, installation, repairment, and maintenance.
Types of Coaxial Cables Used: Commercial-grade coaxial cables tend to be thicker, have a higher copper content, and provide better shielding compared to consumer-level coaxial cables. Examples of commercial coaxial cables include LMR-600, LMR-900, and LMR-1200. Consumer-level coaxial cables, on the other hand, are thinner and have less shielding than commercial cables. Examples of consumer-level coaxial cables include RG-6 and RG-11.
Advantages and Disadvantages: Commercial coaxial cable connectors are designed to support higher frequencies, offer better shielding, and are more durable compared to consumer-level connectors. They are typically used in more demanding applications, such as broadcasting and telecommunications. However, commercial connectors tend to be more expensive than consumer-level connectors and are often more challenging to install.
1. Prices: Commercial coaxial cable connectors are typically more expensive than consumer-level connectors due to their higher quality, better performance, and durability.
2. Applications: Commercial coaxial cable connectors are suitable for radio broadcasting, telecommunications, military, and aerospace applications, which require high-quality, reliable connections. Consumer-level connectors are more commonly used in home entertainment, cable TV, and low-frequency radio equipment.
3. Performance: Commercial connectors offer better performance compared to consumer-level connectors in signal transmit and receive accuracy, noise reduction, and signal strength. This is crucial in broadcasting, where even minor signal degradation can cause significant issues.
4. Structures: Commercial-grade connectors are typically more complex and robust than consumer-grade connectors. They must withstand the rigors of outdoor installations and exposure to the elements, whereas consumer-level connectors are typically used indoors and are less exposed to environmental factors.
5. Frequency: Commercial coaxial cable connectors support higher frequencies compared to consumer-level connectors, which are designed mainly for low-frequency applications.
6. Installation, Repairment, and Maintenance: Commercial coaxial cable connectors require more expertise to install, repair, and maintain compared to consumer-level connectors, which are relatively easy to install and repair. Commercial-grade connectors often require specialized tools, training, and equipment to work with.
In summary, commercial coaxial cable connectors offer higher-quality and better performance compared to consumer-level coaxial cable connectors, but they typically come at a higher cost and require a more extensive installation, repairment, and maintenance process. The selection of a suitable connector depends on the specific application, the types of coaxial cables to be used, and the frequency range required. In broadcasting, commercial-grade connectors are generally preferred due to their durability, performance, and reliability.
- What are common coaxial cable connectors for broadcast transmitters?
- There are several types of coaxial cable connectors available for broadcasting transmitters across different frequency bands (FM, AM, TV, UHF, and VHF). The types of connectors used on these transmitters depend on factors such as the power level of the transmitter and the specific application. Here are some of the most commonly used connector types in broadcasting:
1. N-Type: N-type connectors are commonly used for medium to high power transmitters in FM and TV broadcasting applications. They offer high performance and reliability and can handle high power levels.
2. 7/16 DIN: 7/16 DIN connectors are widely used in high-power FM and TV broadcasting applications. They offer high reliability, high power handling capacity, and low VSWR.
3. BNC: BNC connectors are typically used for low to medium-power FM and TV broadcasting applications. They offer good performance up to 4 GHz and are easy to install.
4. TNC: TNC connectors are used for low to medium-power applications in FM, AM, and TV broadcasting. They are similar to BNC connectors but offer better performance up to 11 GHz.
5. F-Type: F-Type connectors are commonly used for low to medium-power applications in TV broadcasting and cable TV networks. They are easy to install and offer good performance up to 1 GHz.
6. SMA: SMA connectors are typically used in low to medium-power broadcasting applications in the VHF and UHF frequency ranges. They offer high performance up to 18 GHz and are widely used in wireless communication systems.
In terms of how the coaxial cable connector connects to the transmitter, it will depend on the type of connector used on the transmitter. The connection should use the same type of connector on both the transmitter and the coaxial cable. This ensures optimal performance and reliable signal transmission.
In summary, the types of coaxial cable connectors used for broadcasting transmitters depend on the frequency band and the power level of the transmitter. The most common connector types used in broadcasting include N-type, 7/16 DIN, BNC, TNC, F-Type, and SMA. Each type of connector has unique characteristics, such as frequency range, power handling, and ease of installation, which make them suitable for specific applications.
- What are common coaxial cable connectors for rigid transmission lines?
- There are several types of coaxial cable connectors available for rigid transmission lines, and the size of the connector varies depending on the diameter of the coaxial transmission line. Here are some of the most commonly used connector types for rigid transmission lines:
1. Type N: Type N connectors are commonly used with 7/8" and 1-5/8" coaxial transmission lines. They feature a threaded coupling and are designed for use up to 11 GHz. Type N connectors are commonly used in mobile and marine communication applications.
2. 7/16 DIN: 7/16 DIN connectors are designed for use with 1/2", 7/8", 1-1/4", and 1-5/8" coaxial transmission lines. They offer low VSWR and are rated for high power applications. 7/16 DIN connectors are commonly used in wireless and telecommunications applications.
3. EIA: EIA connectors are a series of connectors designed for use with rigid coaxial transmission lines of various sizes, including 1-5/8", 3-1/8", and 4-1/16". EIA connectors have a flanged design and are commonly used in broadcasting and telecommunications.
4. DIN: DIN connectors are designed for use with rigid coaxial transmission lines of various sizes, including 7/8", 1-5/8", 3-1/8", and 4-1/16". DIN connectors have a threaded coupling and are commonly used in wireless and telecommunications applications.
5. LMR-Connectors: LMR-Connectors are designed for use with flexible LMR coaxial cables and their rigid equivalent cables, such as LCF and Superflex. These connectors have a unique construction that allows them to be used with both flexible and rigid coaxial cable.
6. C-Form: C-Form connectors are designed for use with rigid coaxial transmission lines of various sizes, including 2-1/4", 3-1/8", 4-1/16", and 6-1/8". They have a flanged design and are commonly used in high-power broadcasting and communications applications.
The differences between these connector types mostly come down to the size of the connector and the type of transmission line it is designed to work with. They will also differ in the frequency range, power handling capacity, and VSWR performance. When selecting a connector for a particular rigid transmission line, it is important to consider the compatibility of the connector with the transmission line, the operating frequency of the system, and the power requirements of the application.
- What may fails a coaxial cable connector from working?
- There are several situations that can cause a coaxial cable connector to fail, including improper installation, improper maintenance, and environmental factors. Here are some of the most common reasons why coaxial cable connectors may fail, and how you can avoid these situations:
1. Improper Installation: Improper installation is one of the most common causes of coaxial cable connector failure. When connectors are not installed correctly, they can cause signal loss, intermodulation, or even damage to the RF system.
To avoid improper installation, it is important to follow the manufacturer's installation instructions carefully. Use the recommended tools and techniques to prepare the cable and the connector, and make sure that the connector is securely attached to the cable without any gaps or air pockets. It is also essential to use the appropriate torque or pressure when tightening the connector to ensure a proper connection.
2. Corrosion and Moisture: Corrosion and moisture can cause coaxial cable connectors to fail over time. These factors can damage the metal components of the connector, leading to resistance and signal loss.
To avoid corrosion and moisture buildup, use high-quality connectors that are designed specifically for your intended application. Additionally, consider using weatherproofing materials such as sealant or tape to protect the connector from moisture and other environmental factors.
3. Environmental Factors: Environmental factors such as harsh weather conditions, high humidity, and extreme temperatures can cause coaxial cable connectors to fail.
To avoid the effect of environmental factors, it is essential to select the proper type of connector that is designed to withstand the specific environmental conditions or to provide appropriate protection. It is wise to use weatherproof connectors, which are specifically designed to offer protection against weather and other environmental factors.
4. Damage: Physical damage from accidental impacts or excessive bending can also cause coaxial cable connectors to fail.
To avoid physical damage, take care when handling coaxial cables – avoid sharp bends and twists that may cause damage to the cable or connector. Protect the cable and connector from physical stress by using protective materials, such as cable wraps and strain reliefs.
In summary, to avoid coaxial cable connector failure, it is crucial to follow the manufacturer's instructions for installation, use the appropriate tools, and select connectors appropriate for the environment and application. Regular maintenance, such as inspecting the connections for signs of corrosion and moisture buildup, can also help prevent failures and ensure reliable performance.
- How to correctly use and maintain a coaxial cable connector?
- Proper use and regular maintenance can help ensure the long-life expectancy of a coaxial cable connector. Here are some tips on how to correctly use and maintain a coaxial cable connector:
1. Use the Appropriate Connector for Your Application: The coaxial cable connector must match the cable type, impedance, and frequency range to work correctly. Using the wrong connector or mismatching connector components can lead to increased signal loss and reduced performance.
2. Use the Appropriate Tools for Installation: Always use the right tools to install your connector properly. Incorrect tools can damage the connector or cable and weaken the connector's performance.
3. Follow Installation Instructions: Follow the manufacturer's instructions carefully when installing your connector. Be sure to trim the cable to the recommended length, match the center conductor and insulator, and tighten the connector to the recommended torque.
4. Protect Against Environmental Factors: Environmental factors like moisture, temperature fluctuation, and extreme weather conditions can damage the connector and reduce its life-expectancy. Use weatherproofing materials like sealant and protect the connector from weather or physical stress using enclosures or cable management systems.
5. Inspect and Maintain Regularly: Inspect the cable and connector frequently for signs of damage and ensure connectors are tight enough to avoid signal loss. Remove dust and debris, wipe off moisture, and use contact cleaning spray for dirty connectors.
6. Replace Damaged Connectors: If you notice any damage or corrosion, replace the coaxial cable connector immediately. Check any loose fitting, disconnecting, or noise this could be the solution to improve the performance of your coaxial cable.
By following these recommendations, you can help to maximize the life-expectancy and performance of your coaxial cable connectors, ensure reliable signal transmission, and reduce the chances of signal loss and interference.
- How to choose the best coaxial cable connector for FM broadcasting?
- Choosing the right coaxial cable connector for FM broadcasting depends on several factors related to the specific application, transmitter output power level, frequency range, coaxial cable types, and antenna classifications. Here are some key considerations that can help you choose a suitable connector:
1. Application: Consider the specific application for the coaxial cable connector you need. For example, in an FM broadcasting system, you may require connectors with high power handling capacities and reliable connections. Also, consider the operating frequency and signal quality required for the application, as this will impact connector quality.
2. Transmitter output power level: You need to consider the power level of your transmitter output as you will require a connector that can handle the power level without impacting the signal quality. Generally, high power connectors such as 7/16 DIN connectors or Type N connectors are suitable for high-power FM broadcasting applications.
3. Frequency Range: Ensure the connector you choose is designed to work across the entire frequency range required for your FM broadcasting application. BNC and TNC connectors are suitable for low-frequency applications up to 4 GHz. While 7/16 DIN connectors and Type N connectors are more suitable for higher frequency applications up to 11 GHz.
4. Coaxial cable types: Different types of coaxial cables have different impedance levels, core diameters and power-handling capabilities. Different coaxial connectors are suitable to connect different types of coaxial cables. Ensure the connector you choose is compatible with the type of coaxial cable you have.
5. Antenna classifications: Different types of antennas require different types of coaxial cable connectors. For example, a dipole antenna usually requires a BNC or TNC connector, while circularly polarized antennas may require a Type N connector or 7/16 DIN connector.
In summary, when choosing the best coaxial cable connector for FM broadcasting, it is important to consider the application, transmitter output power, frequency range, coaxial cable type, and antenna classifications. Also consider the reliability and quality of the connector, as well as factors such as price and availability when selecting a connector that best fits your requirement.
CONTACT US

FMUSER INTERNATIONAL GROUP LIMITED.
We are always providing our customers with reliable products and considerate services.
If you would like to keep touch with us directly, please go to contact us