
- Home
- Product
- CATV Headend
- FMUSER IPTV to 16/32/48 Clear Channel RF QAM / ATSC Modulator
- DTV Headend Equipment
-
Control Room Console
- Custom Tables & Desks
-
AM Transmitters
- AM (SW, MW) Antennas
- FM Broadcast Transmitters
- FM Broadcast Antennas
-
Broadcast Towers
- STL Links
- Full Packages
- On-Air Studio
- Cable and Accssories
- Passive Equipment
- Transmitter Combiners
- RF Cavity Filters
- RF Hybrid Couplers
- Fiber Optic Products
-
TV Transmitters
- TV Station Antennas
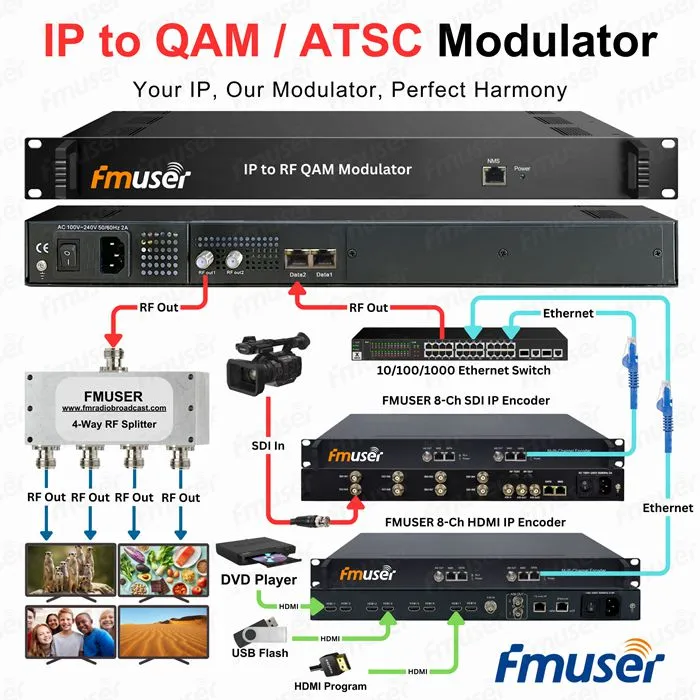

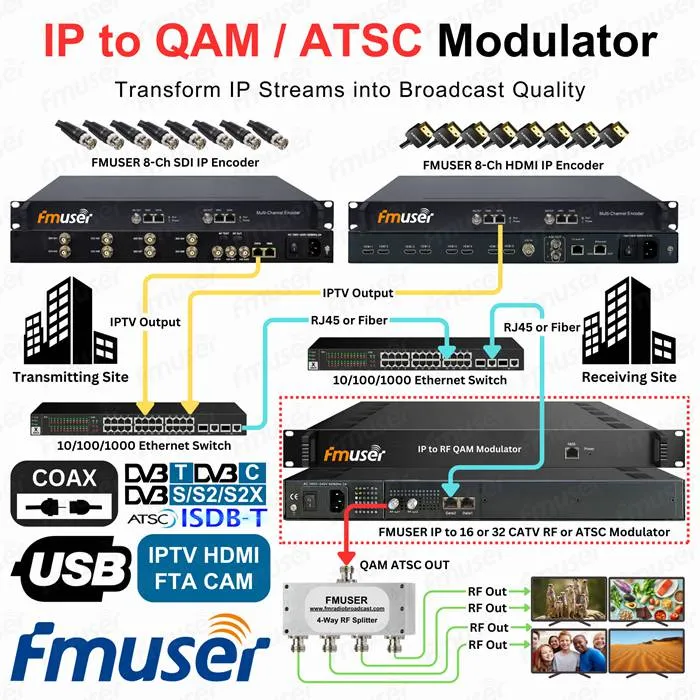

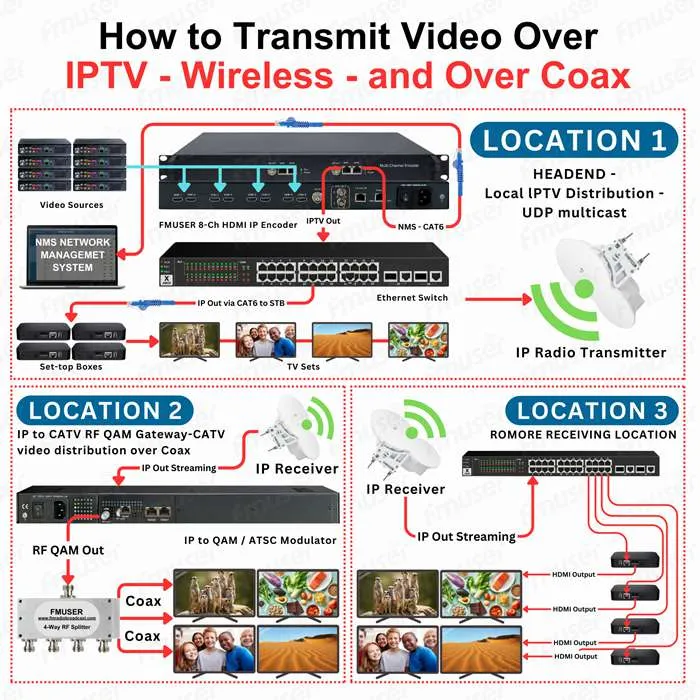
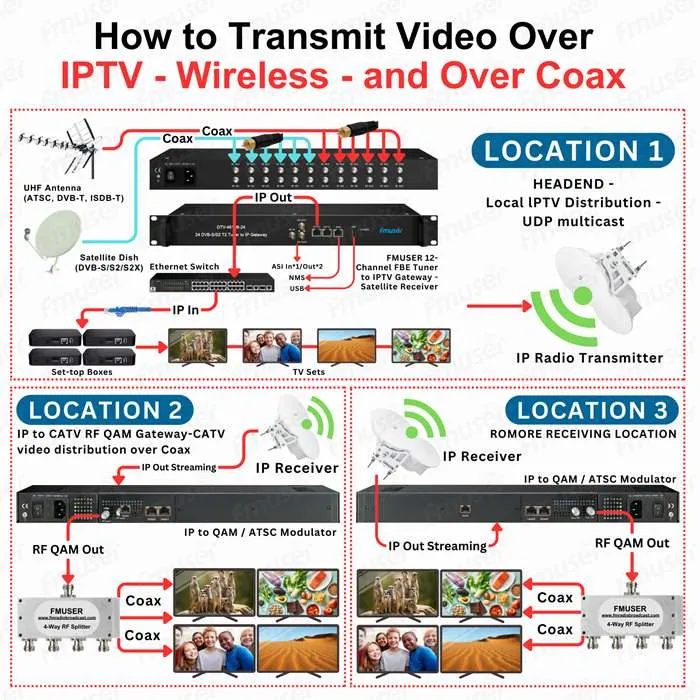
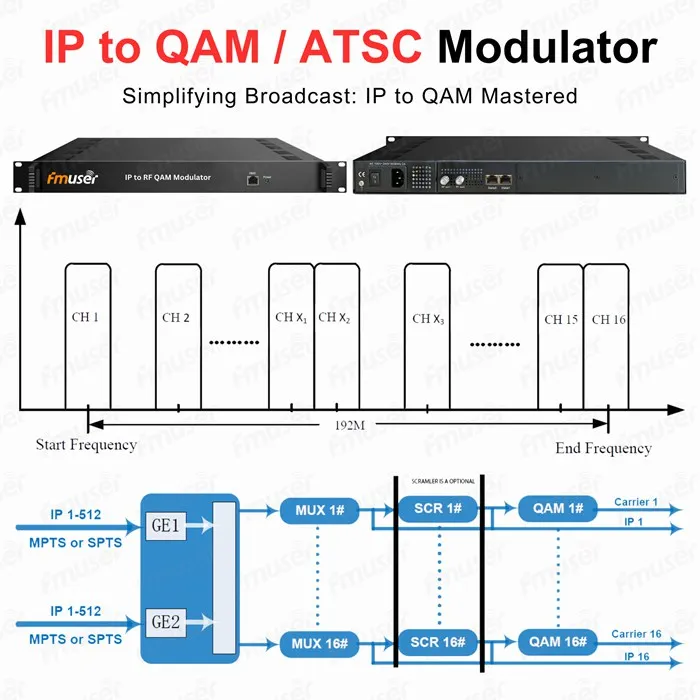


FMUSER IPTV to 16/32/48 Clear Channel RF QAM / ATSC Modulator
FEATURES
- Input Available at: IP/IPTV, Software Management Available
- Output Available at: RF / QAM / DVB-T / ATSC / ISDB-T
- Applications: All in one headend unit for SMATV systems in residential blocks, hotels, offices etc.
- Availability: In-Stock and Ship Today
- Wholesale Discount: Yes
- Shipping Method: DHL, FedEx, UPS, EMS, By Sea, By Air
- Payment: TT(Bank Transfer), Western Union, Paypal, Payoneer
Description
The FMUSER IPTV to 16/32 Clear Channel RF QAM/ATSC Modulator delivers unmatched density for CATV and broadcast networks, seamlessly converting up to 1024 UDP/RTP IP streams into 16 non-adjacent DVB-C or ATSC-compliant QAM/ATSC RF channels within a compact 1RU chassis.

Designed for system integrators seeking professional-grade scalability, this edge QAM modulator supports dual Ethernet inputs with 840Mbps throughput per port, enabling high-bandwidth 4K-ready content distribution via a unified RF F-type output for simplified coax integration. Leveraging industry-standard IGMP v2/v3 multicast protocols, it efficiently transcodes IPTV feeds into crystal-clear QAM/ATSC signals—ideal for building cost-effective IP-to-RF headends or upgrading legacy infrastructure.

Centralized management is streamlined through an intuitive web-based GUI accessible via the front-panel NMS port, allowing real-time configuration of IP inputs, channel mapping, and RF parameters. As one of the best modulators for IPTV-to-QAM conversion, FMUSER’s solution combines carrier-class reliability with future-ready flexibility, empowering operators to deploy scalable digital cable, hospitality, or MDU services while minimizing rack space.

For integrators prioritizing performance and density, this IP QAM modulator ensures seamless compatibility with existing IPTV ecosystems—contact FMUSER today to explore how its 32-channel expansion capability can future-proof your RF delivery network.
Model Selection
- IP to 16/32 QAM Clear Edge RF Modulator
- IP to 8/16 ATSC Clear Edge RF Modulator
- IP to 8/16 DVB-T Clear Edge RF Modulator
- IP to 8/16 ISDB-T Clear Edge RF Modulator
Get Exactly the Cable Headend You Need
Tired of juggling clunky IPTV setups? Our FMUSER Modulator is here to simplify your life. Think of it as your all-in-one tool for turning IPTV streams (yes, even 4K!) into crystal-clear QAM or ATSC cable channels. Whether you need a handful of HD channels or a full lineup of SD programming, this box gives you the flexibility to build your dream channel lineup—without the headache.

1. Why This Modulator?
- Bandwidth Magic: It takes incoming IP streams, optimizes every bit of bandwidth, and transforms them into up to 16 or 32 RF channels. Need more HD? Fewer SD? Your call.
- No Channel Left Behind: Mix and match frequencies with non-adjacent QAM configurations. Your headend, your rules.PID Control Freak? Auto or manual PID remapping lets you fine-tune channel setups like a pro.
- Speed Demon: Each Gigabit Ethernet port handles up to 840Mb/s—enough to fuel 16 QAM channels without breaking a sweat.

2. We’re Not Just Modulator People
FMUSER specializes in full broadcast ecosystems. From Hybrid Fiber Coax (HFC) to Fiber to the Home (FTTH), we’ve got the gear and know-how to handle projects big or small. Our team doesn’t just sell boxes—we design custom solutions. Stuck on a technical puzzle? Our engineers love a good challenge and will work with you to find answers (even ones you didn’t know existed).

3. Here’s the Best Part
This isn’t a one-size-fits-all product. Let’s chat about your project! Our sales team offers free consultations to design a system tailored to your needs. Maybe you’re upgrading an old headend, launching a new hotel TV system, or diving into 4K broadcasting. Whatever it is, we’ll help you nail it.
Feature Overview
1. Integrated Web Management System
Our web management system streamlines the configuration and monitoring of IP-to-QAM Edge Modulators with an intuitive web portal interface. Designed for multimedia distributors, it centralizes frequency setups, IP multicast configurations, and real-time stream diagnostics, ensuring seamless integration and efficient network management.
* NMS Setup WEB Page GUI: Frequency setup page in FMUSER IP to QAM Edge modulator
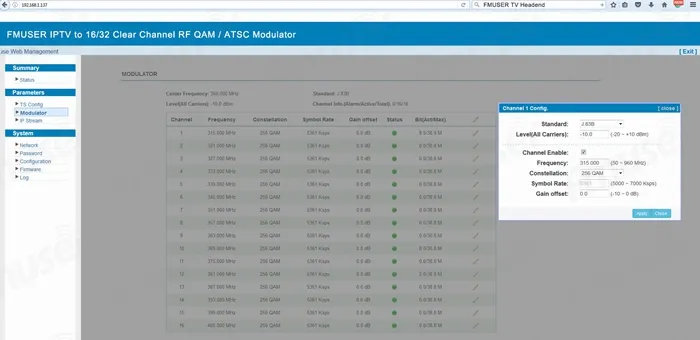
.
* NMS Setup WEB Page GUI: IP multicast Input to setup page IP to QAM Edge Modulator settings.
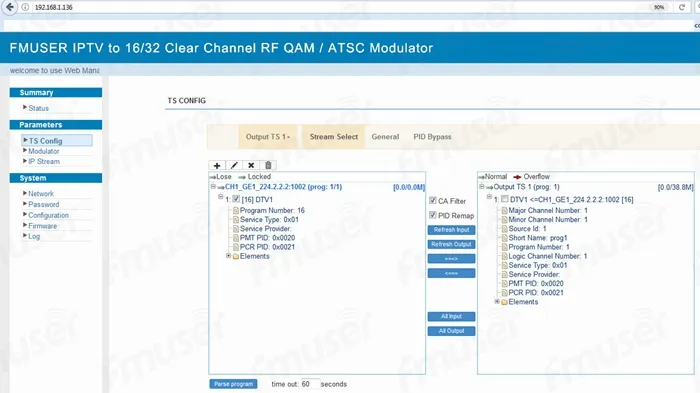
1. High-Density IP-to-RF Signal Conversion
Engineered for CATV and broadcast networks requiring scalable 4K-ready solutions, this edge QAM modulator transforms up to 1024 IP streams into 16/32 non-adjacent QAM/ATSC RF channels, minimizing rack space while maximizing output flexibility.

Ideal for system integrators deploying IPTV-to-coax infrastructures, it ensures seamless integration with existing IPTV ecosystems.
- 1024 TS over IP Capacity: Convert UDP/RTP unicast/multicast streams into 16 DVB-C or ATSC-compliant RF channels (expandable to 32), supporting high-density content aggregation.
- Clear Channel Output: Distribute non-adjacent QAM/ATSC signals across 50-960MHz with carrier-grade stability, ideal for CATV headends or MDU distribution.
- PID Remapping Flexibility: Automatically or manually manage up to 180 PIDs per channel, ensuring compatibility with legacy or custom RF systems.
2. High-Performance Network Integration
Optimized for bandwidth-intensive 4K workflows, this IP QAM modulator leverages dual Gigabit Ethernet inputs to deliver 840Mbps throughput per port, ensuring uninterrupted IPTV content delivery.

- Dual Gigabit Ethernet Ports: Redundant SFP interfaces support multicast/unicast IGMP v2/v3, enabling fail-safe IPTV stream ingestion.
- 840Mbps per Input: Handle ultra-HD content with minimal latency, ideal for high-demand broadcast or hospitality networks.
- Advanced Protocol Support: Compatible with RTP, UDP, and multicast protocols for seamless integration into IPTV/CDN backbones.
3. Professional-Grade RF Output Control
Designed as a best-in-class RF modulator, this solution provides precise control over QAM/ATSC signal parameters, enabling operators to optimize broadcast quality and compliance.
- Multiplexed & Scrambled Outputs: Generate up to 32 RF channels with optional scrambling for secure content delivery.
- Wide Frequency Range: Output signals across 50-960MHz, supporting global CATV and ATSC standards.
- Unified RF Interface: Simplify coax integration with a single F-type connector, reducing cabling complexity.
4. Centralized Management & Scalability
FMUSER’s edge QAM modulator includes an intuitive web-based NMS for real-time monitoring and configuration, streamlining deployment and maintenance.
- Web NMS GUI: Remotely configure IP inputs, channel mapping, PID settings, and RF parameters via a browser-based interface.
- Future-Ready Expansion: Scale from 16 to 32 QAM/ATSC channels with software licensing, adapting to growing network demands.
- Real-Time Diagnostics: Monitor throughput, signal health, and error logs to ensure uninterrupted service delivery.
As a leading IP-to-QAM transcoder, this modulator combines carrier-class reliability with unmatched density, making it the best modulator for IPTV-to-RF conversion. System integrators benefit from its 1RU form factor, 4K readiness, and compliance with ATSC/DVB-C standards—perfect for upgrading legacy systems or building cost-effective digital headends.
Specifications.
| input | input | 512 × 2 IP inputs, 2x 100 / 1000M Ethernet port (SFP) | |
| input | Transport Protocol | TS over UDP / RTP unicast and multicast, IGMP V2 / V3 | |
| input | Transmission Rate | Max 840Mbps for each input GE | |
| mux | Channel input | 1024 | |
| mux | Output Channel | 16 | |
| mux | max PIDs | 180 per channel | |
| mux | Functions | PID remapping (auto / manually optional) | |
| mux | Functions | PCR accurate adjusting | |
| mux | Functions | PSI / SI table Automatically generating | |
| Scrambling parameters | Max simulscrypt CA | 4 | |
| Scrambling parameters | Scramble Standard | ETR289, ETSI 101 197, ETSI 103 197 | |
| Scrambling parameters | Connection | Local / remote connection | |
| Modulation parameters | QAM Channel | 16 non-adjacent carriers | |
| Modulation parameters | Modulation Standard | EN300 429 / ITU-T J.83A / B | |
| Modulation parameters | symbol Rate | 5.0 ~ 7.0Msps, stepping 1ksps | |
| Modulation parameters | Constellation | 16, 32, 64, 128, 256QAM | |
| Modulation parameters | FEC | RS (204, 188) | |
| RF Output | Interface | 1 F-type output for 16 carriers, 75Ω impedance | |
| RF Output | RF Range | 50 ~ 960MHz, stepping 1kHz | |
| RF Output | Output Level | -20dBm ~ + 10dBm (~ 87 117dbμV), 0.1dB stepping | |
| RF Output | MAYOR | ≥ 40dB | |
| RF Output | ACLR | -60 dBc | |
| TS output | 16 IP output over UDP / RTP / RTSP, unicast / multicast, 2 x 100 / 1000M Ethernet Ports | ||
| System | Network management software (NMS) | ||
| General | Dimensions | 420mm × 440mm × 44.5mm (WxLxH) | |
| General | Weight | 10lbs | |
| General | Temperature | 0 ~ 45°C (Operation) -20 ~ 80°C (Storage) | |
| General | Power Supply | AC 100V ± 10%, 50 / 60Hz or 220V AC ± 10%, 50 / 60Hz | |
| General | Consumption | 15.4W | |
FMUSER 4-Channel IP-to-RF Streaming Modulator: Compact CATV Edge QAM Solution
FMUSER’s advanced 4-channel streaming live modulator delivers seamless IP-to-RF conversion, transforming UDP/RTP transport streams into up to four agile RF QAM/ATSC carriers. Designed for system integrators, this RF CATV modulator supports MPEG-2, H.264, and other encoding formats—ensuring output channels retain the original video/audio specifications. Equipped with dual RJ45 ports, it dedicates one to IP input (unicast/multicast) and the other to streamlined NMS integration for remote monitoring and channel configuration. The edge QAM modulator efficiently multiplexes multiple IP streams into a single RF carrier, optimizing bandwidth utilization (e.g., 38 Mbps in QAM 256 accommodates 12+ programs at 3.5 Mbps each). Built-in Virtual Channel Tables (VCT) enable custom numbering and naming, while global preloaded RF standards ensure compatibility across regions. Ideal for cost-effective IP-to-cable conversion, this compact RF QAM modulator simplifies deployment in hotels, campuses, and broadcast networks, offering scalability and professional-grade reliability. Enhance your live streaming infrastructure with FMUSER’s modular solution—engineered to future-proof local TV systems and drive viewer engagement.
Main Features
FMUSER’s streaming live modulator bridges IP and RF worlds, offering a future-proof solution to convert UDP/multicast streams into broadcast-ready CATV/QAM signals. Engineered for system integrators, this IP QAM modulator simplifies large-scale deployments with robust signal customization, global compliance, and scalable output—ideal for hotels, MDUs, and digital headends.
1. Advanced IP Streaming Input & Management
Maximize flexibility with support for diverse IP sources and protocols, ensuring seamless integration into existing workflows.
- Multi-Protocol IP Input Support: Accept UDP, RTP, unicast, or multicast streams with IGMPv2/v3 compatibility for efficient network resource utilization.
- Scalable IP Input Capacity: Process up to 63 unique IP inputs (SPTS) simultaneously, ideal for multi-channel environments.
- Enhanced Network Flexibility: Dedicated data ports for streaming and NMS ensure secure, isolated management without signal interference.
2. Broadcast-Grade Signal Customization
Tailor signals for compliance or localized requirements with precision editing tools.
- Dynamic PID Filtering & Remapping: Modify CA PIDs, remap streams, or strip/insert PSI/SI tables to meet regional standards.
- PSI/SI Table Editing: Customize program-specific metadata for accurate EPG and channel organization.
- CA System Integration: Securely align encrypted streams with conditional access requirements.
3. Multi-Channel RF CATV/QAM Modulation
Deliver stable, high-quality RF output across four agile carriers.
- Simultaneous Multi-Carrier Output: Generate 4 continuous RF channels (QAM, ATSC, ISDB-T) with configurable frequencies and bandwidths.
- Bandwidth-Efficient Multiplexing: Combine multiple IP streams into a single RF carrier (e.g., 38 Mbps QAM 256 supports 12+ HD programs).
- Virtual Channel Management: Assign custom VCT numbers and names for intuitive viewer navigation.
4. Global Modulation Standards Support
Deploy anywhere with preloaded regional broadcast standards.
- ATSC/DVB-C Annex B: Optimized for North America and Mexico.
- ISDB-T Compliance: Ready for Latin America and Japan.
- DVB-T/T2/C Annex A/C: Full coverage for EMEA markets.
5. Simplified Deployment & Control
Reduce setup time and costs with intuitive tools and compact hardware.
- Web UI Configuration: Adjust settings remotely via browser-based interface for rapid provisioning.
- Compact Plug-and-Play Design: Save space and reduce shipping costs with a lightweight, rack-mountable chassis.
- Dedicated NMS Port: Monitor device health and performance in real time using SNMP or third-party tools.
Specifications
| IP INPUT | |
| Input Connector | 1x 100/1000Mbps port |
| Transport Protocol | UDP, RTP |
| MAX Input IP Address | 63 channels |
| Input Transport Stream | SPTS |
| Addressing | Unicast and Multicast |
| IGMP Version | IGMP v2 and v3 |
| RF OUTPUT | |
| Output Connector | 1x RF female 75Ω |
| Output Carrier | 4 agile RF channels |
| Output Range | 50 ~ 999.999MHz |
| Output Level | ≥ 45dBmV |
| Out-band Rejection | ≥ 60dB |
| MER | Typical 38 dB |
| DVB-C J.83A | |
| Bandwidth | 6M, 7M, 8M |
| Constellation | 64QAM, 256QAM |
| Symbol Rate | 3600 ~ 6960 KS/s |
| DVB-T | |
| Bandwidth | 6M, 7M, 8M |
| Constellation | 16QAM, 64QAM |
| Code Rate | 1/2, 2/3, 3/4, 5/6, 7/8 |
| Guard Interval | 1/4, 1/8, 1/16, 1/32 |
| FFT | 2k, 4k, 8k |
| Symbol Rate | 6000,7000,8000 KS/s |
| ATSC | |
| Bandwidth | 6M, 7M, 8M |
| Constellation | 8VSB |
| DVB-C J.83B | |
| Bandwidth | 6M, 7M, 8M |
| Constellation | 64QAM, 256QAM |
| Symbol Rate | Automatically |
| DTMB | |
| Bandwidth | 8M |
| Constellation | 16QAM, 32QAM 64QAM,QAM_4NR |
| Interleave Mode | NONE, 240 ,720 |
| FEC | 0.4, 0.6 ,0.8 |
| Carrier Type | Multi or Single |
| Sync Frame | 420, 549, 595 |
| PN Phase | Variable or Constant |
| Work Mode | Manual or Preset |
| MULTIPLEXING | |
| Table Supported | PSI/SI |
| PID Processing | Pass-through, Remapping, Filtering |
| Dynamic PID Feature | Yes |
| GENERAL | |
| Input Voltage | 90 ~264VAC, DC 12V 2A |
| Power Consumption | W |
| Rack Space | Compact Wall or Desk Mount |
| Dimension (WxHxD) | 178 x 32 x 124mm / Length: 7 inches Width: 1.25inches Height: 4.9inches |
| Net Weight | 0.68KG |
| Language | English |
32-Channel IP to CATV RF Gateway with Integrated H.264 to MPEG2 Transcoding
FMUSER’s 32-Channel IP-to-CATV RF Gateway integrates advanced H.264-to-MPEG2 transcoding with edge QAM modulation, offering a future-proof solution for broadcasters and system integrators addressing compatibility challenges in North America. While H.264 dominates IP and satellite streaming, legacy CATV networks across the U.S., Canada, and Mexico rely on MPEG2 video paired with Dolby AC3 audio for RF signal transmission. This device bridges the gap by efficiently transcoding live IP streams—such as those from satellite gateways or IPTV platforms—into MPEG2-compliant formats, ensuring seamless playback on legacy TVs and QAM tuners. With adjustable bitrates (1–19 Mbps), it supports flexible bandwidth optimization for high-quality HD content delivery. The integrated RF QAM modulator enables multi-channel output across DVB-C, ATSC, ISDB, and DVB-T/T2 standards, making it ideal for large-scale CATV, hospitality, or MDU deployments. Featuring IP input and RF output ports, this streaming live modulator simplifies signal distribution while eliminating compatibility bottlenecks. Designed for reliability, it supports edge QAM modulation, clear QAM, and ATSC standards, empowering integrators to future-proof legacy systems, reduce infrastructure costs, and scale IP-to-RF workflows effortlessly. Whether deploying IPTV modulators, RF CATV modulators, or hybrid QAM converters, FMUSER’s solution ensures broadcast-grade performance for mission-critical applications—contact us to optimize your signal distribution strategy.
Elevate Your Signal Distribution with Advanced IP-to-RF Transcoding & Modulation
FMUSER’s 32-Channel IP-to-CATV RF Gateway revolutionizes broadcast workflows by combining high-density transcoding, edge QAM modulation, and flexible signal management into a single platform. Designed for system integrators managing hybrid IP and RF environments, this solution ensures seamless compatibility with legacy CATV infrastructure while optimizing bandwidth for modern HD content delivery. Below, explore its core capabilities grouped into critical functional categories:
1. High-Capacity Signal Processing & Transcoding
Engineered to handle large-scale IP-to-RF workflows, this gateway supports up to 64 IP stream inputs, transcoding H.264 video and AAC/MPEG audio into MPEG2 formats for flawless compatibility with North American QAM tuners. Ideal for converting satellite, IPTV, or OTT streams into CATV-ready signals.
- Multi-Format Transcoding: Convert H.264 IP streams to MPEG2 video and Dolby AC3 audio, ensuring legacy TVs decode signals without issues.
- Resolution Flexibility: Supports SD to Full HD (480i to 1080p60), adapting to source quality while maintaining broadcast standards.
- Dynamic Bandwidth Control: Adjust transcoded bitrates from 1–19 Mbps per channel, balancing quality and bandwidth efficiency.
2. Precision RF Modulation & Channel Management
As a versatile streaming live modulator, the device integrates an edge QAM modulator to distribute signals across 32 RF channels, compatible with DVB-C, ATSC, ISDB, and DVB-T/T2 standards.
- 32-Channel RF Output: Deliver up to 32 continuous QAM RF channels, with dual-program multiplexing per channel for efficient spectrum use.
- Clear QAM & ATSC Compliance: Ensure compatibility with cable headends and consumer TVs using standardized modulation (J.83B, ClearQAM).
- PSI/SI Table Editing: Remap PIDs, edit program metadata, and customize service information for accurate EPG and channel organization.
3. Streamlined Configuration & Monitoring
Simplify deployment and maintenance with intuitive tools designed for system integrators.
- Web-Based Management: Configure settings, monitor status, and troubleshoot via an integrated web UI—no specialized software required.
- CA PID Filtering: Securely manage conditional access systems by filtering or remapping PIDs for encrypted content distribution.
- Scalable Architecture: Expand workflows effortlessly with a modular design suited for hospitality, MDUs, or municipal broadcast networks.
Specifications
| IP INPUT | |
| Input Connector | 100/1000Mbps port |
| Transport Protocol | UDP, RTP |
| MAX Input IP Address | 64 |
| Input Transport Stream | MPTS and SPTS |
| Addressing | Unicast and Multicast |
| IGMP Version | IGMP v2 and v3 |
| RF OUTPUT | |
| Output Connector | 1x RF female 75Ω |
| Output Carrier | 32 agile channels |
| Output Range | 50 ~ 999.999MHz |
| Output Level | ≥ 45dBmV |
| Out-band Rejection | ≥ 60dB |
| MER | Typical 38 dB |
| DVB-C J.83A | |
| Bandwidth | 6M,7M,8M |
| Constellation | 64QAM,256QAM |
| Symbol Rate | 3600 ~ 6960 KS/s |
| DVB-T | |
| Bandwidth | 6M,7M,8M |
| Constellation | QPSK,16QAM,256QAM |
| Code Rate | 1/2, 2/3, 3/4, 5/6, 7/8 |
| Guard Interval | 1/4, 1/8, 1/16, 1/32 |
| FFT | 2k, 4k, 8k |
| Symbol Rate | 6000,7000,8000 KS/s |
| ATSC | |
| Bandwidth | 6M,7M,8M |
| Constellation | 8VSB |
| DVB-C J.83B | |
| Bandwidth | 6M,7M,8M |
| Constellation | 64QAM,256QAM |
| Symbol Rate | Automatically |
| TRANSCODING | |
| INPUT | |
| Video Resolution | Up to 1080p_60 fps |
| Video Form | MPEG1/2/4; H.264; H.265; AVS; AVS+; VC1 |
| Audio Form | MPEG-1 Layer I/II/III; WMA, AAC, AC3 |
| OUTPUT | |
| Video Transcoding | H.264 to MPEG 2 or MPEG2 to H.264 |
| Audio Transcoding | MPEG 1/ AAC / AC3 |
| Resolution | Downscaling to preset one |
| MULTIPLEXING | |
| Table Supported | PSI/SI |
| PID Processing | Pass-through, Remapping, Filtering |
| Dynamic PID Feature | Yes |
| GENERAL | |
| Input Voltage | 90 ~264VAC |
| Power Consumption | W |
| Rack Space | 2RU |
| Dimension (WxHxD) | 19"x3.4"x17" (482*88*430mm) |
| Net Weight | 20lb |
| Language | English |
Why Choose FMUSER?
This IP QAM modulator bridges the gap between modern IP streaming and legacy RF infrastructure, empowering integrators to future-proof networks while reducing costs. Whether deploying IPTV modulators, RF CATV modulators, or hybrid QAM converters, its 32-channel capacity and multi-standard support ensure reliable, high-density signal distribution.
Advanced Edge QAM Modulator for Seamless RF & IP Broadcast Integration
This professional-grade edge QAM modulator from FMUSER enables ASI input-to-output program management, decoding, and distribution via IP and RF interfaces simultaneously. Designed for CATV, satellite, and IPTV systems, it features robust RF QAM modulation capabilities, supporting clear QAM outputs alongside encrypted streams for versatile content delivery. Engineered to process Transport Streams from encoders, multiplexers, DVB gateways, and video servers, this RF QAM modulator ensures reliable signal conversion with enhanced error correction, making it ideal for demanding applications like live broadcasting, interactive services, and news gathering. Its dual-output architecture allows concurrent IP streaming and RF transmission, providing unmatched flexibility for hybrid network deployments. Compatible with edge QAM and ATSC standards, the unit integrates seamlessly into existing workflows and supports remote management through centralized NMS platforms, reducing operational complexity. Built for scalability, this modulator IPTV solution delivers broadcast-grade performance for cable headends, broadband satellite systems, and multiscreen distribution, empowering integrators to future-proof their infrastructure while maintaining cost efficiency. FMUSER’s modulator QAM technology guarantees low-latency, high-stability outputs, ensuring premium video quality for mission-critical operations.
Model Selection
- ASI to QAM Digital modulator
- ASI to ATSC Digital modulator
- ASI to DVB-T Digital modulator
- ASI to ISDBT Digital modulator
Key Features
1. Standards Compliance & Modulation Flexibility
This edge QAM modulator adheres to global broadcasting standards, ensuring compatibility with existing infrastructure while offering adaptable modulation modes. System integrators benefit from seamless integration and future-proof performance across diverse applications.
- DVB-C & ATSC Compliance: Fully compliant with DVB-C (EN300 429), ITU-T J.83A/B/C, and ATSC standards for universal compatibility.
- Wide Symbol Rate Range: Adjustable symbol rates from 5.0Msps to 9.0Msps for optimized bandwidth utilization.
- Multi-Constellation Support: 16QAM to 256QAM modes, enabling tailored signal quality and bandwidth efficiency.
2. Advanced Signal Processing & Output Control
Precision signal handling and dual-output capabilities make this QAM RF modulator ideal for hybrid IP/RF workflows, minimizing latency and maximizing reliability.
- Dual IP/RF Outputs: Simultaneously transmit via RF (30MHz–1000MHz) and IP (RTP, RTSP, UDP) for flexible distribution.
- PCR Adjustment & PID Filtering: Ensure timing accuracy and bandwidth optimization with PCR correction, PID remapping, and PSI/SI updates.
- Intelligent TS Processing: Automatically deletes null packets, inserts NIT data, and manages burst streams with a large buffer memory.
3. Network Management & Operational Efficiency
Simplified control and monitoring via web-based interfaces ensure seamless integration into modern broadcast ecosystems.
- Web NMS & SNMP Support: Remote configuration and real-time monitoring via SNMP or browser-based interfaces.
- LCD & Keyboard Operation: On-device controls for quick adjustments in field deployments.
- Output Attenuation Control: Fine-tune RF output levels (-16dBm to +12dBm) in 0.5dB steps for optimal signal strength.
4. Security & Scalability
Designed for secure, scalable deployments, this modulator IPTV solution supports evolving content protection needs.
- Integrated Scrambler: Safeguard content with built-in encryption for secure transmission.
- Future-Ready Architecture: Easily scales to support growing channel counts and emerging standards.
Specifications
| Input | 1channel ASI input, BNC interface, 75Ω | |
| Modulation | QAM or ATSC or DVB-T or ISDBT Channel (model depandent) defalt unit comes with QAM Modulation | 1 |
| Standard | EN300 429/ITU-T J.83A/B/C | |
| Symbol Rate | 5.0~9.0Msps 1ksps stepping | |
| Constellation | 16/32/64/128/256QAM | |
| FEC | RS(204, 188) | |
| RF Output | Connector | F Type, 75Ω impedance |
| RF Range | 30~1000MHz 1kHz Stepping | |
| Output Attenuation | -16dBm ~ +12dBm 0.5dB Stepping | |
| IP Output | IP output in UDP/RTP/RTSP - SPTS/MPTS, Unicast/Multicast | |
| System | LCD/keyboard operating and NMS support | |
| English | ||
| Software update via Etherent | ||
| General | Dimension(W*D*H) | 482mm × 300mm × 44mm |
| Weight | 2.3kg | |
| Temperature | 0~45°C (Operation) ;-20~80°C (Storage) | |
| Power | AC 110V±10%/50/60Hz or AC 220V±10% /50/60Hz | |
| Consumption | 22W | |
Why Choose FMUSER?
FMUSER’s edge QAM modulator empowers system integrators to streamline hybrid broadcast environments with unmatched flexibility and reliability. Whether deploying clear QAM modulator signals for cable headends or integrating IPTV solutions, its dual-output design and enterprise-grade management tools reduce operational complexity while ensuring premium performance. Elevate your infrastructure with a QAM RF modulator built for tomorrow’s challenges—contact us today to explore tailored solutions.
CONTACT US

FMUSER INTERNATIONAL GROUP LIMITED.
We are always providing our customers with reliable products and considerate services.
If you would like to keep touch with us directly, please go to contact us



